ARCHITECTURE
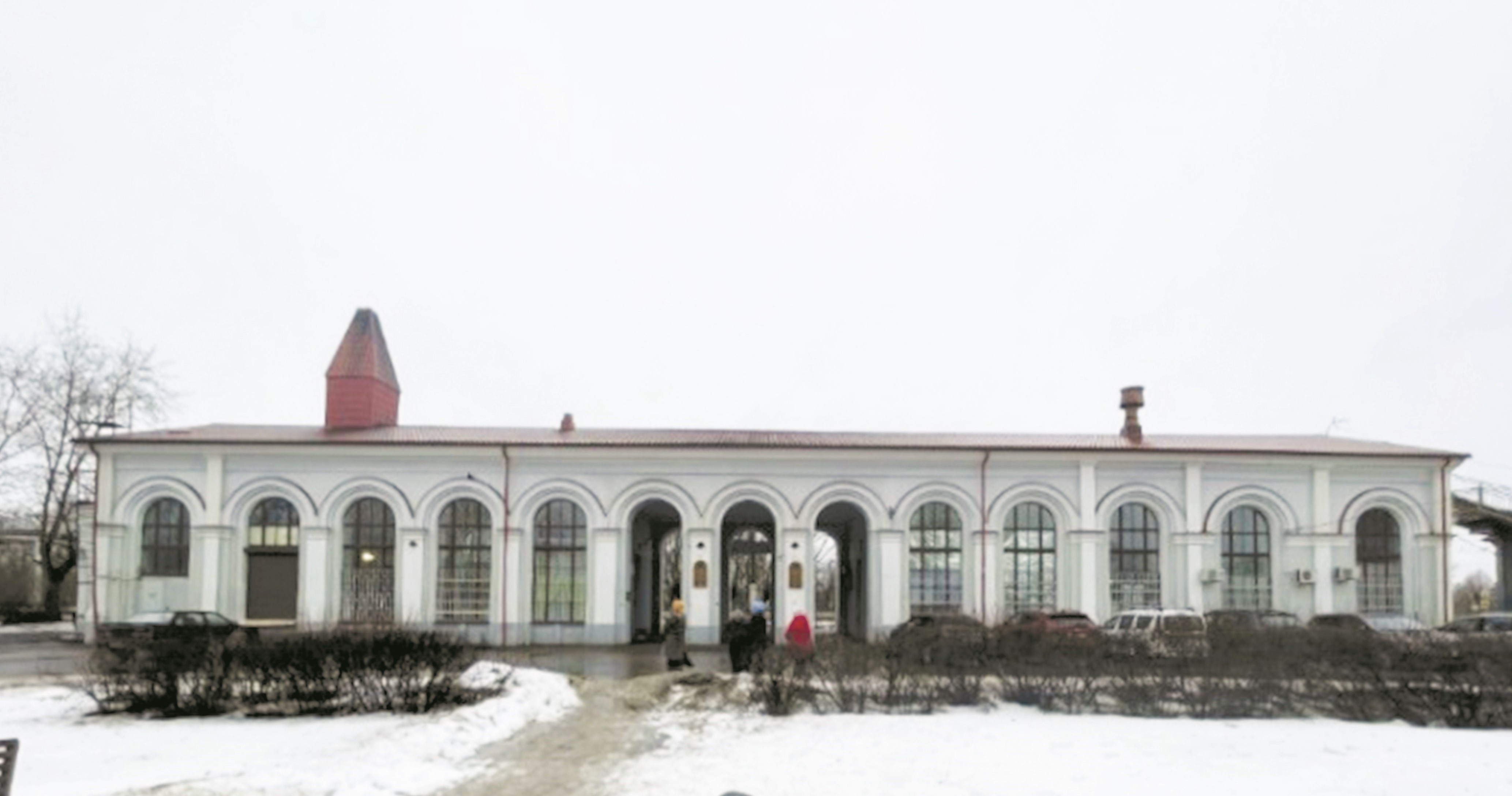
This study is based on the author’s historical and cultural research into the architectural complex of railway stations between Saint Petersburg and Gatchina on the Saint Petersburg–Warsaw Railway. The research examined the history of Alexandrovskaya station’s construction from 1852 to 1854, under the guidance of architect, Titular Counselor K. A. Skardzhinsky and responsible for work execution E. I. Gerstfeld during the construction of Tsarist Russia’s first international railway line. It also investigated the station’s subsequent reconstruction, destruction, and loss in the early 20th century. The research confirmed the principle of standardized design for railway facilities in terms of planning and spatial characteristics. To determine the historical and cultural value of the research object, the composition of the station buildings along the section of railway under study was established, along with their priority and structural hierarchy within the complex. The study identified the stylistic features and principles that shaped the complex of Alexandrovskaya station, providing the basis for its inclusion on the list of identified cultural heritage sites.
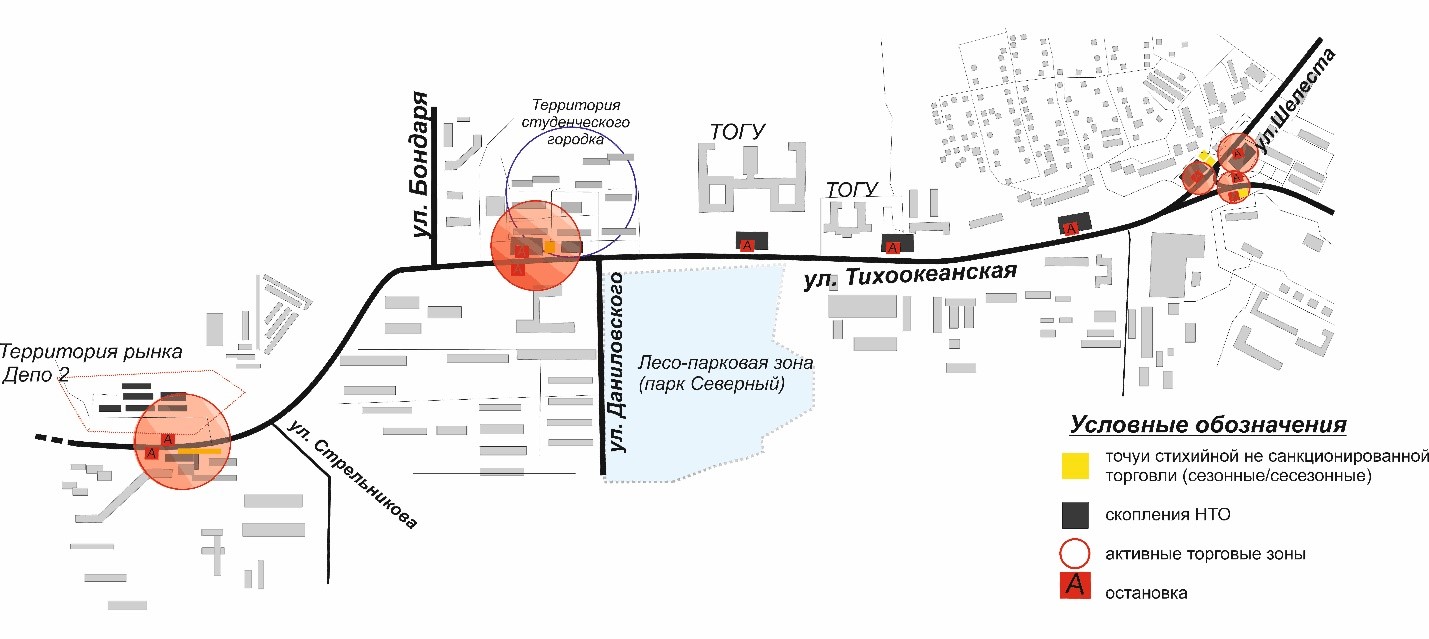
This study examines the organization of retail modules and linear retail structures in Khabarovsk, that shaping public perception of accessible, high-quality goods and services. The paper considers the linear retail structures along Tikhookeanskaya Street, one of the major transportation artery connecting numerous mobile and stationary retail outlets. Employing a mixed-methods approach – incorporating comparative, cartographic, and field research – allow us to identify main features of linear retail structures, analyze key challenges in retail placement, explore planning scenarios, and examine architectural and spatial arrangements of non-stationary retail outlets that promote accessibility for city residents. The study proposes architectural solutions for existing street retail modules, such as facades made of perforated or mesh panels with decorative designs or murals. It also presents design proposals for non-stationary retail structures to enhance the city’s aesthetic appeal. One project – wrought-iron ice cream kiosks – has already been implemented, while another is a student-designed concept for a retail complex inspired by fair marquees. These solutions aim to preserve regional identity and offer a rational planning approach within the context of necessary urban densification.
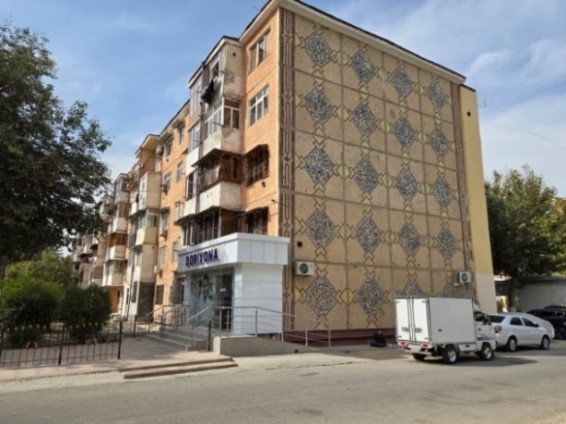
This paper presents the findings of urban development studies conducted in Samarkand (Republic of Uzbekistan), using the Sattepo residential area as a case study. The contribution of Samarkand’s precast concrete factories, which constructed the microdistrict with 5- and 9-story lightweight expanded clay concrete panel residential buildings from enlarged wall panels of popular standardized series 1-464, 148, and 1-474, was examined. The artistic mosaic decoration of these buildings imparts a unique national character to these standardized Soviet-era housing developments and has a historical cultural value, continuing to impress residents and visitors to Uzbekistan. Such research is needed to find a balance between the preservation of authentic cultural values and the possibility of architectural modifications in Samarkand for its continued development.
CONSTRUCTION
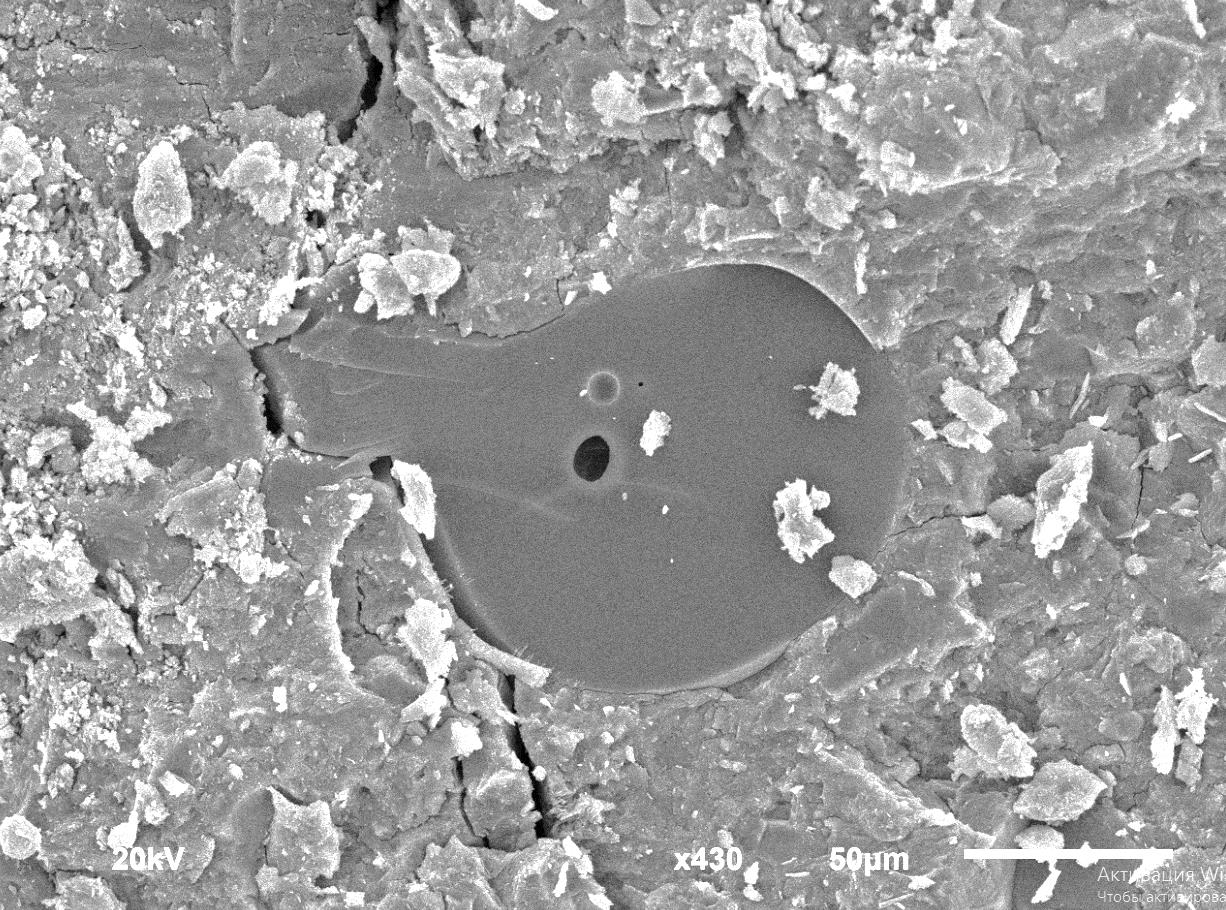
Reinforcing components and chemical additives are significant in modifying the structure of cement composites. Ceramic fibers, as a disperse-reinforcing component in cement systems, provide increased tensile strength in bending, crack resistance and durability of the material. The results of the research have revealed that such a concrete structure-forming component as ceramic mullite-silica fiber 0.02 to 0.06 mm across is rational to combine with a carboxylates-based chemical additive. Optimal dosages of mullite-silica fiber that influence the structure and physical-mechanical properties of the cement stone were determined. The method of scanning electron microscopy and spectral analysis was used to examine processes on the interface cement matrix – fiber. It has been underlined that fibers are covered by phase-forming hydrates due to structural and chemical correspondence. The use of ceramic fibers of high-temperature synthesis and water-reducing additive made it possible to increase the compressive strength of cement composites by 1.9 times compared to the control sample, as well as to improve the resistance of cement stone to destruction by increasing the bending tensile strength by 3.9 times and crack resistance by 2 times compared to the control composition.
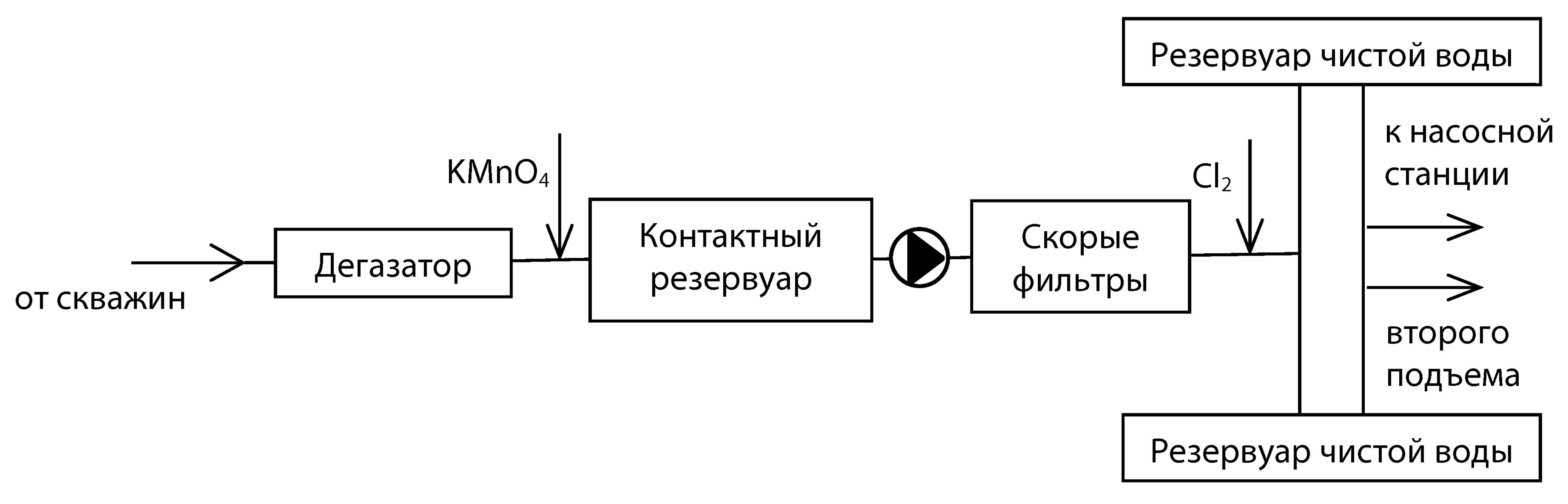
This article presents a reconstruction plan for an underground water deferrization station in southern of Tyumen Oblast, including a feasibility study. The reconstruction is necessary due to unsatisfactory water quality delivered to consumers, primarily high manganese content. Analysis of the initial and treated water quality from the existing plant revealed key factors affecting the treatment processes. The proposed technological modifications consider the groundwater’s unique composition, in particular, the high dissolved carbon dioxide leading to low pH, along with the operational experience of region deferrization stations and results from laboratory and pilot-scale testing at similar facilities. The proposed solution uses a reagent method for manganese removal, employing potassium permanganate as an oxidant. To reduce carbon dioxide concentration and increase pH, the study recommends replacing the aeration system from vacuum-ejector to barbotage in the loading layer. The reconstruction does not require an increased facility size. Technological calculations take into account maximum use of the existing station. The feasibility study determined capital and operating costs, and calculated the increase in water supply costs. The assessment of reconstruction efficiency demonstrated its economic viability.
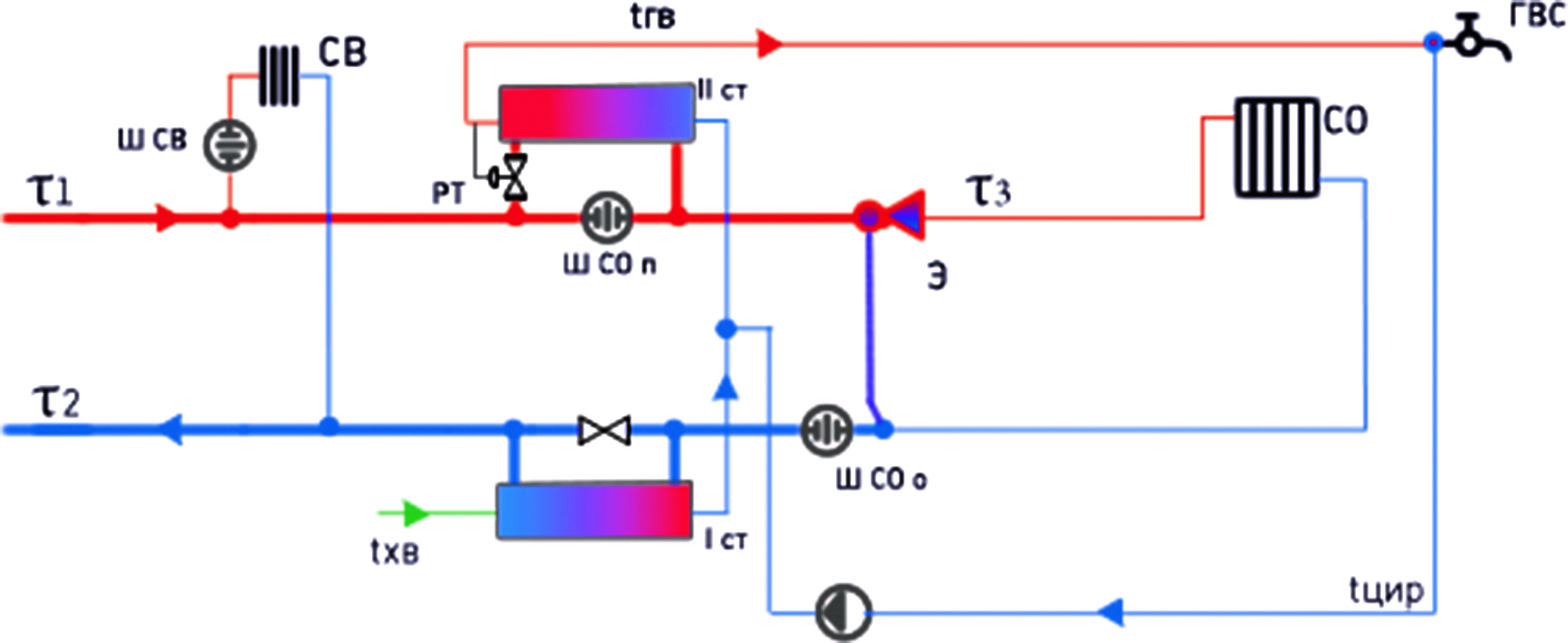
Modernizing the heat supply sector involves improving both the reliability and safety of heating systems and enhancing service quality for end users. To achieve these aims, Tyumen launched a program in 2021 to transition from central to individual heat points. The study examined four main heating connection schemes, which account for over 80% of city connections. Switching from these standard schemes to individual heat points offers several advantages. Management companies gain the ability to efficient manage heat supply directly in each building. End users gain greater control, allowing them to choose optimal parameters for heating and hot water, leading to cost optimization and reduced utility bills. This paper presents a case study of a Tyumen multifamily residential building that successfully transitioned from a central to an individual heat point. Consumers saw a 4% reduction in costs during the first month of the heating season. Furthermore, even a single building’s conversion to an individual heating substation allows the heat supply organization to reduce heat network reconstruction costs by 2%. Based on this analysis, the transition is deemed a success.
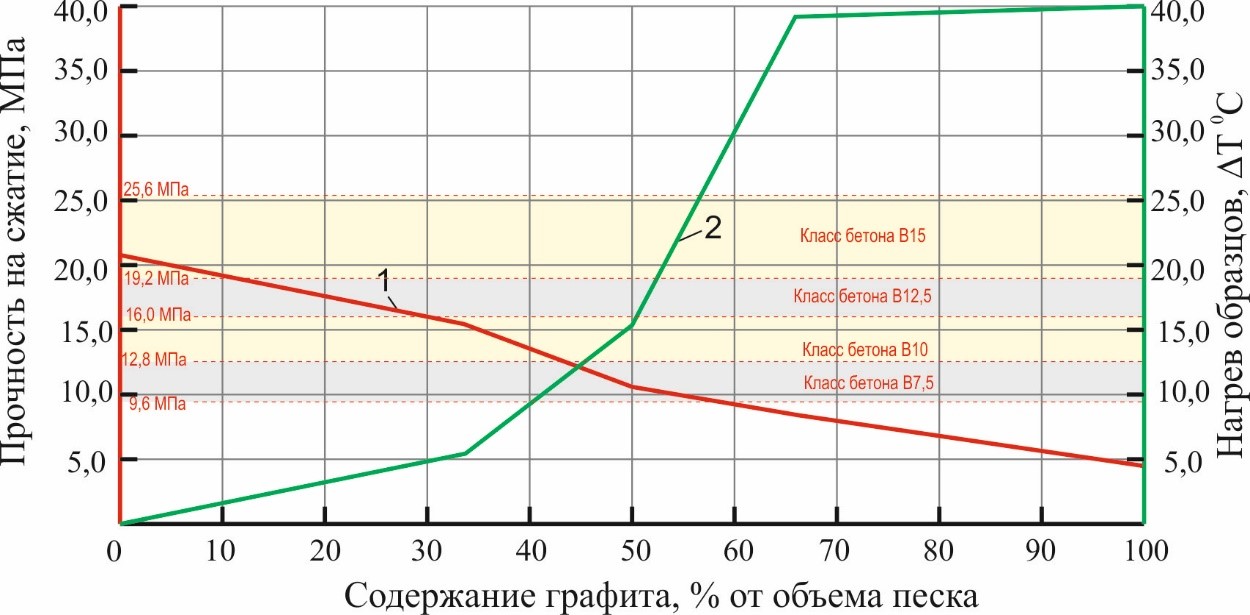
In civil and road construction, the service life of structures is heavily influenced by the quality and properties of the construction and road-building materials used. Improving the properties of existing and commonly used materials, particularly concrete, is a high research priority. This work aims to produce electrically conductive concrete using carbonaceous additives and to assess the effect of these additives on compressive strength. The research focused on cement concrete mixes containing graphite. Laboratory testing was conducted in four stages. In the first stage, B15 concrete mixes were designed, considering the specific characteristics of the components. Based on the developed formulations, the second stage of the research involved the production of a series of heavy B15 concrete samples with varying graphite content: 0%, 33%, 50%, 66%, and 100%. The third stage involved compressive strength testing of the samples while saturated with water. Finally, the electrical and thermal characteristics of the graphite-containing samples were evaluated. Analysis showed that increasing graphite content improves electrical conductivity, enabling electrical heating of the concrete However, increased graphite content also reduces compressive strength. The practical significance of this work lies in the development of electrically conductive concrete mixes that meet specified strength requirements.
TRANSPORT
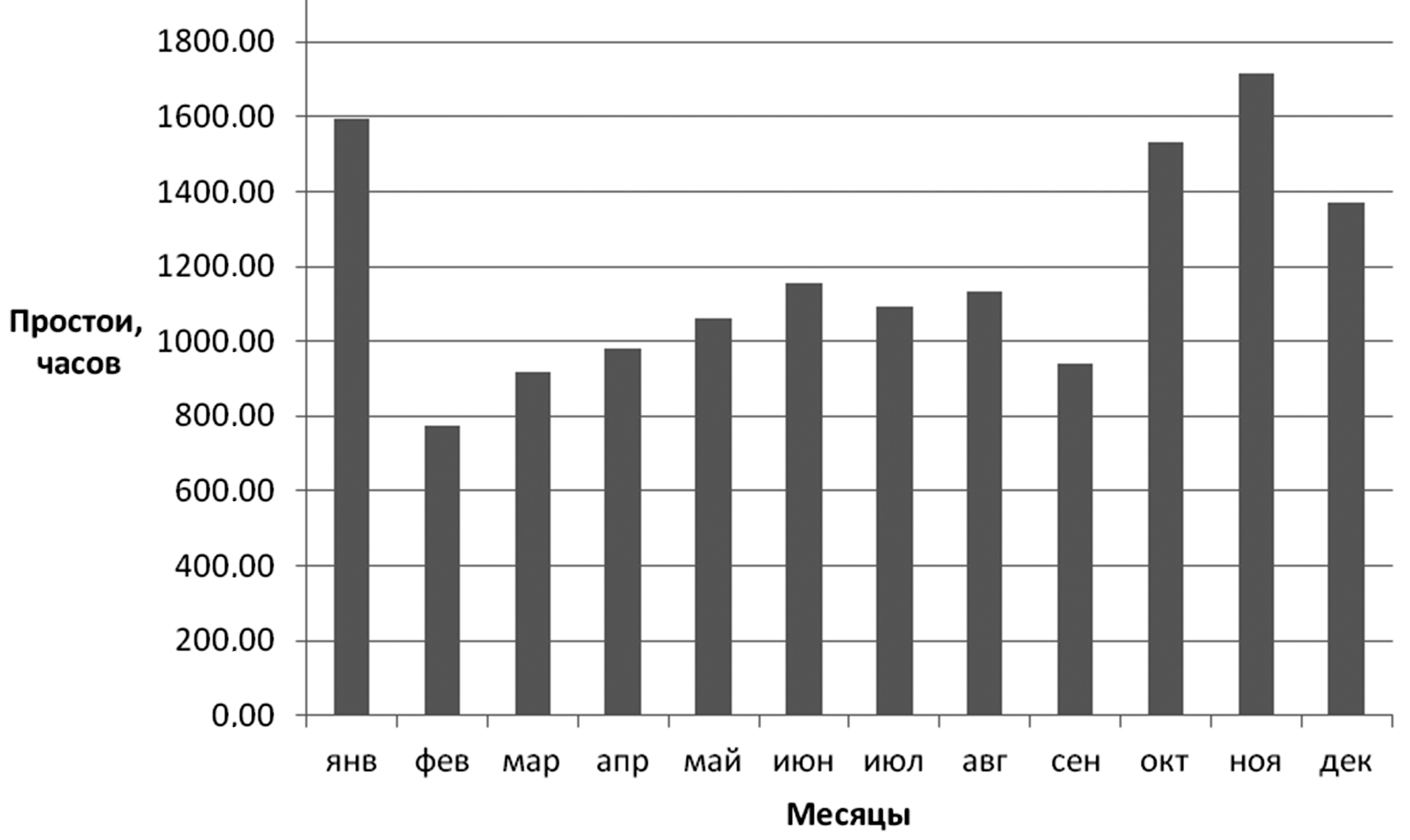
This study addresses the increasing number of failures, downtime, and maintenance and repair costs associated with BelAZ 7513 and 7530 series haul trucks operating in the extreme climatic conditions of Khakassia’s coal mines. An assessment of the actual specific downtime for these trucks during repair and maintenance reveals values ranging from 3 to 60 hours per 100 operating hours, significantly exceeding the 14-15-hour standard for Khakassia’s cold climate. A method of temperature correction for maintenance frequency during winter was proposed to reduce scheduled maintenance frequency and the volume of unscheduled repairs. This study further proposes improvements to the maintenance and repair system for BelAZ haul trucks in cold climates, considering truck age, low temperatures, and a reliability analysis of the truck design. To optimize this system, the implementation of a digital twin for the transportation enterprise was suggested. This digital twin will enable individualized maintenance scheduling for each haul truck, adjusting the frequency of all maintenance procedures based on negative air temperatures. The digital twin will also facilitate the integration of additional maintenance list into the scheduled maintenance plan, thereby minimizing unscheduled repairs and equipment failures.
VECTOR OF SCIENCE
Modern bridge construction demands efficient designs, technologies, and materials. Traditional methods tend towards simpler designs, whereas modern approaches enable a wider variety of structures and architectural forms. This research explores successful examples of 3D printing, bionics and fractal approaches in bridge engineering, and analyzes the potential of combining these technologies for optimal results in modern bridge construction.
This study aimed to improve the methodology for evaluating the research activities of engineering master’s students. Criterion-based evaluation is one of the main tools for assessing the development of research competences. Based on data from professional experts and relevant regulatory documents, evaluation criteria for student research were defined. Parameters for a credit-based evaluation system were introduced. The methodology proposed for calculating a composite research assessment provides a holistic and objective evaluation of the research conducted, independent of the opinions of supervisors or individuals.
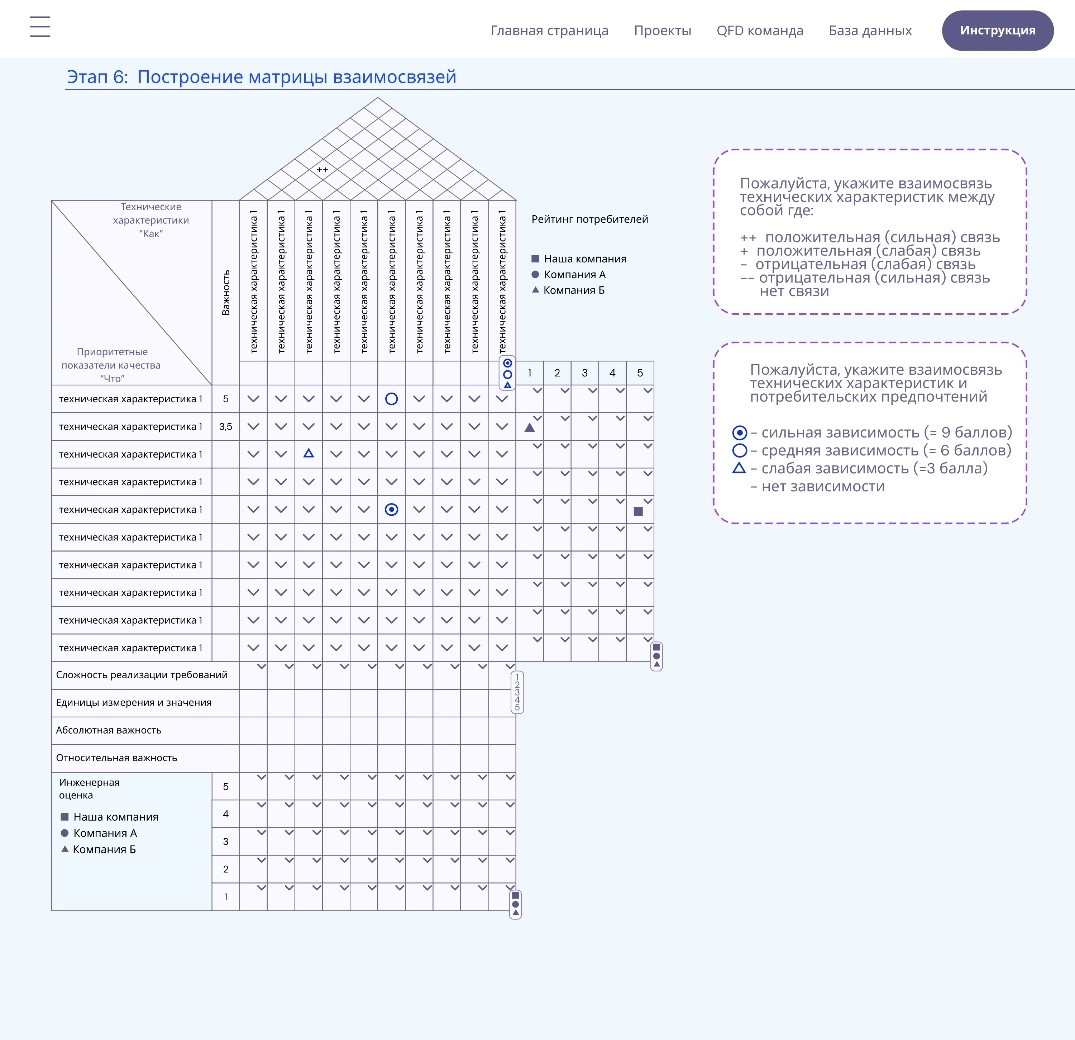
QFD analysis is among the few quality tools that can encompass a wide range of processes in product manufacturing. This analysis enables effective planning for the implementation of various technical support tools, which complement each other in prioritizing each problem - product imperfections and low competitiveness. A significant drawback of QFD analysis is the considerable time and effort required to construct the final table/matrix, known as the "house of quality". The study investigated existing solutions aimed at reducing analysis time and identified the main parameters for their implementation. Based on the collected data, the key strengths and weaknesses of existing solutions were identified, and a web application was developed. This article aimed to develop an online application that simplifies and accelerates QFD analysis. The developed application facilitates the automation of the QFD analysis process, significantly enhancing the efficiency of quality management professionals and reducing the time required for this procedure.
ISSN 2713-0770 (Online)