ARCHITECTURE
The work considers residential buildings with administrative functions (office, commercial, banking, etc.) in the city of Tyumen of the late XIX – early XX centuries. Planning solutions and architectural and decorative details of these objects of the city's historical development are analyzed. It is established that there were mostly brick and stone two-storied residential buildings (the first floor for work, the second for the owner's living). In addition, there were common features in the facades design: the symmetrical front facade, the geometric attic on the central axis of the front facade, as well as the wide belt separating the floors. Most of these objects have survived until nowadays, but they have lost their original administrative function.
Wood-based building materials meet the basic requirements of environmentally friendly construction, which is becoming increasingly important in the modern world. However, until recently, they were rarely used in high-rise construction in Russia. CLT became a revolutionary technology, it has proven itself in countries such as Switzerland, Norway, the U.S. and others. In Russia, it has not yet found widespread use, and CLT-panels are in demand only at the market of individual housing construction. Nevertheless, taking into account the positive foreign experience can be an example and become an incentive for more active implementation of modern environmentally friendly materials and technologies in Russia. The aim of the article is to study the possibilities of highrise wooden house building in Russia based on world practice.
CONSTRUCTION
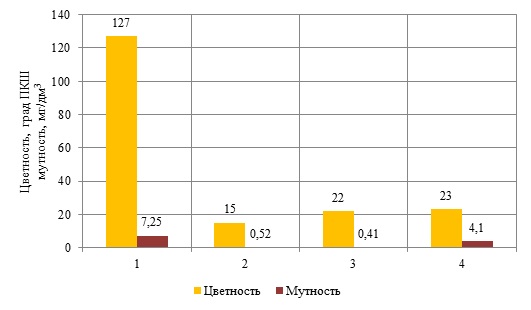
A characteristic feature of the qualitative composition of natural water of the Northern zone of the Tyumen region, regardless of the season, are: low salt content – less than 200 mg/dm3 and suspended solids – 2–30 mg/dm3 , iron content at 0,1-5,5 mg/dm3 , high color – 40–130 ˚ of the platinum-cobalt scale. When eliminating color and complex-bound iron from natural water, the greatest difficulties are associated with low salt content and small values of suspended solids. This predetermines a slightly different from the regulations approach to the choice of technological scheme of water treatment. Based on the results of the research, variants of technological schemes of natural water treatment of the northern rivers are proposed.
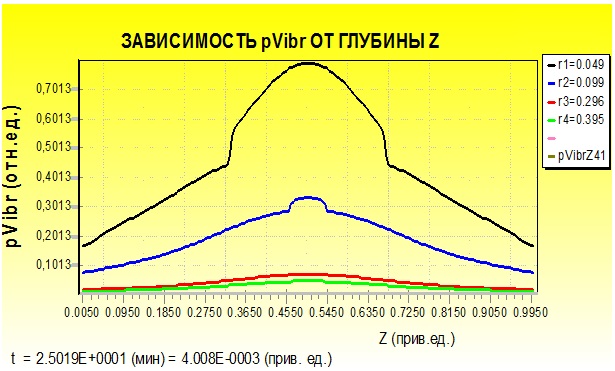
The search for ways of accelerating the preparation of bases on water-saturated boggy areas is an up-to-date problem and requires further scientific study. The conducted researches made it possible to establish that vibration can be an effective means of accelerating the consolidation of water-saturated soils of the bases. Using theoretical and experimental research, a method for numerical solution of the problem was developed.
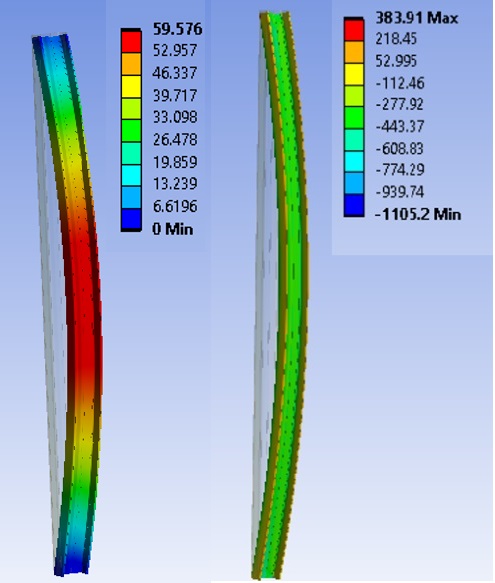
The article describes the process and reflects the results of modeling a steel thin-walled sigma profile operating under axial compression in the ANSYS software. Modeling is carried out taking into account the zones of hardening of steel along the profile section. The results are analyzed and compared with the results obtained in STARK.
The article deals with the main causes of defects in the structural elements of buildings. Their role and influence on the normal implementation by the construction of its functional purpose are shown. The regularity of the formation of defects caused by deviations from the design documentation and disfunction of technological processes is analyzed. Measures to eliminate specific defects requiring a significant increase in labor and material costs are presented.
TRANSPORT
The article deals with the problems of determining the intensity of traffic flows on streets and roads with irregular traffic for the purposes of design, heavy repair, reconstruction and traffic management. The impossibility of using existing monitoring methods at decentralized transport facilities and algorithms for decrypting remote satellite surveillance materials predetermined the necessity of developing a mathematical model within the framework of multifactor forecasting. During the studying of significant factors, the influence of variability in the population density and the capacity of general education facilities was investigated. Identification signs of educational institutions used in the interpretation of satellite images were obtained. The polynomial dependences of the traffic intensity on the specified characteristics were developed. The carried out correlation assessment allows us to talk about the high degree of reliability of results of analytical determination of intensity on the streets with irregular traffic.
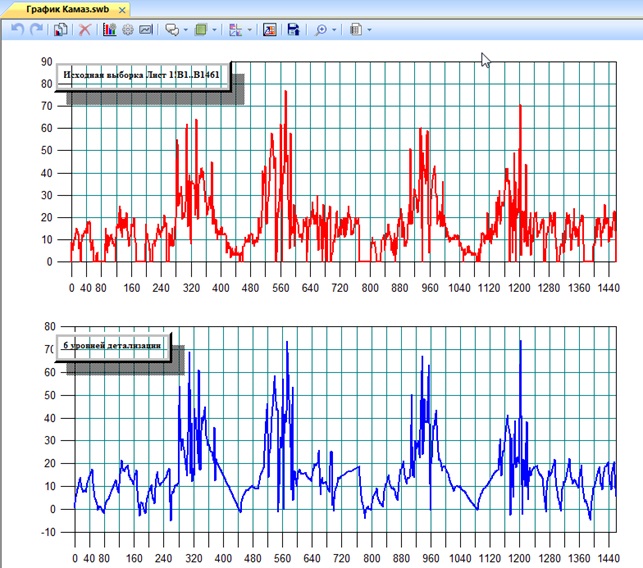
Driving cycles are represented, as a rule, the dependence of speed on the current time, and they are widely used to assess the operational characteristics of road transport, in particular, the fuel efficiency of newly produced and already operated vehicles, as well as their environmental friendliness. Fuel consumption in the urban and mixed cycles is the most important characteristic of the car. This indicator gives an objective assessment of the vehicle's efficiency, but provided that the reference cycle used in its determination corresponds to the real operating conditions. The article considers the problem of determining the characteristics of a typical driving cycle based on the real speed profiles of vehicles obtained as a result of GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite Systems) monitoring.
The reliability of road transport is one of the main factors affecting the operational capacity and special works performance of any road transport company. The efficiency of task performance directly depends on the uninterrupted operation of vehicles at the site of operation.
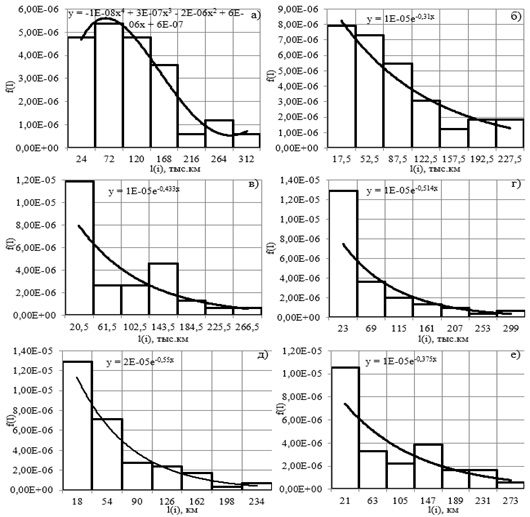
The authors of the study collected data of MTBF of special trucks Ural 4320 for six transmission elements: gearboxes, transfer gearboxes, clutches, cardan shafts, front and rear axles.
The numerical values of the main uptime indicators are determined and their functional dependences on the MTBF are obtained. According to the graphic representation of the functional dependences and variation coefficients, the law of distribution of random variables is determined.
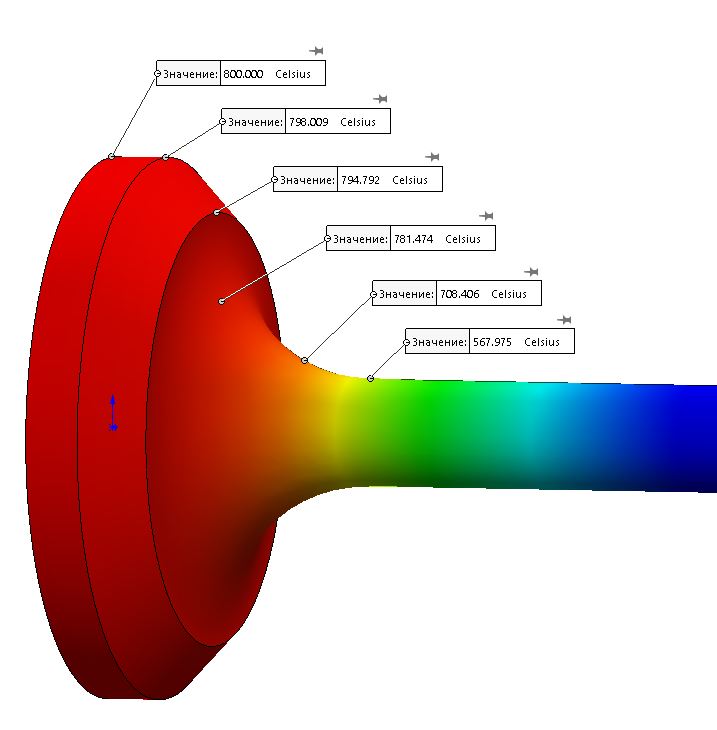
Reducing the heat load of the valve mechanism of the gas distribution system is an urgent task. This is due to the need to reduce the risks of deformation of the working surface of the valve disc and, as a consequence, to increase the resource of the gas distribution mechanism.
The paper proposes a valve mechanism design with the possibility of supplying the coolant to the combustion chamber through the valve cavity. The data from the preliminary study showed the effectiveness of the coolant supply. When comparing the temperature indicators in the test points under study, a decrease in the valve temperature by 0,72– 25 % was revealed.
ISSN 2713-0770 (Online)