ARCHITECTURE
This gap between theoretical knowledge about historical and stylistic design principles and design process is an up-to-date problem of architectural education. During the students teaching, we suggest to implement the interdisciplinary approach, based on the parallel studying of two disciplines: the theoretical analysis of the interior styles evolution and the practical design of living space. Project solutions by third-year students from the department of architectural environment design at the Industrial University of Tyumen were considered as examples. As well as the theoretical and analytical justification of the results obtained was provided. It was established that the students who have received a preliminary theoretical base apply stylistic principles in interior design more competently, without using the intuitive copying. The interdisciplinary approach promotes the required competencies developing, such as artistic and creative thinking, coloristic and visual culture, and the ability to operate with meaning-forming elements of style and adapt them to modern conditions. The research results prove the necessity of studying the theory of architecture and art in the context of their historical development as the basis for the formation of project culture.
CONSTRUCTION
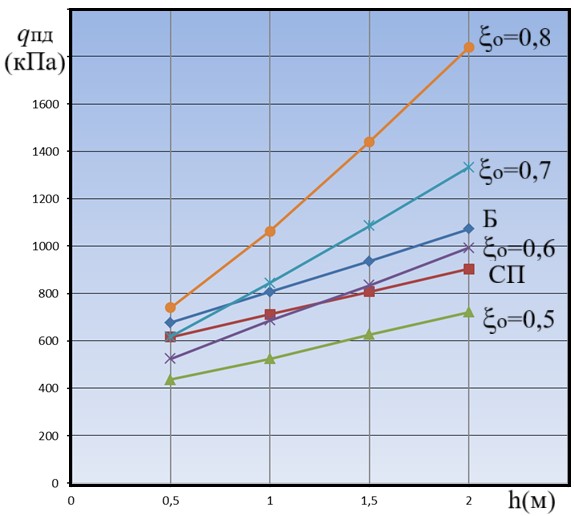
This article presents the calculation results of the bearing capacity of two- and three-slot foundations on a homogeneous base, performed using the FEA computer program, which implements the finite element method. Based on these results, the influence of various factors (foundation embedment depth, distance between the slots, and the lateral earth pressure coefficient of the surrounding soil) on the soil’s stress state and the development of Coulomb plastic deformation zones was assessed. The calculations were performed with a ratio of the reinforced concrete’s modulus of elasticity to the soil’s modulus of deformation equal to 103 , which, as demonstrated in the work, corresponds to a realistic value. It was shown that the use of a threeslotted Ш-shaped foundation is not advisable because it is inferior to a two-slotted П-shaped foundation in both bearing capacity and settlement, under otherwise equal conditions. Analysis of the comparative calculation results indicated that the numerical values of the bearing capacity for a two-slot foundation, calculated according to SNiP and SP recommendations, can be reproduced using the FEA program for specific values of the lateral soil pressure coefficient. Consequently, the FEA computer program is recommended for use in relevant calculations.
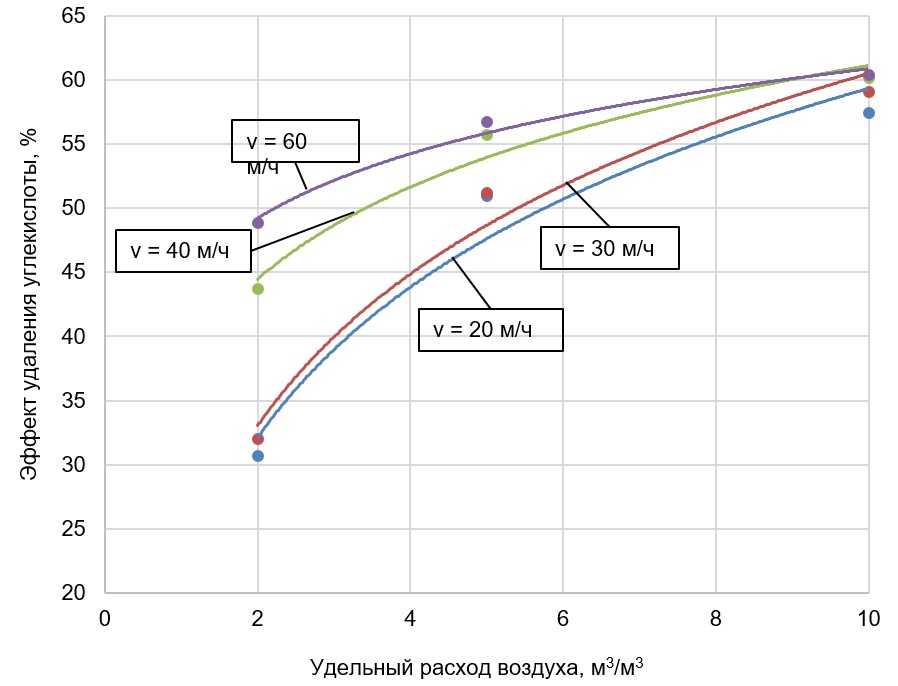
Physical desorption, achieved through water bubbling in a free volume, is a fairly effective method for removing dissolved gases, particularly carbon dioxide. Bubbling degassers are characterized by their technological effectiveness, simple design, and reliable operation regardless of the season. In some cases, studies of bubbling plants are theoretical in nature and don’t take into account most of their physicochemical composition parameters and design features of the units. As a result, the calculation equations become approximations for laboratory data or recommendations with additional conditions. Physical phenomena, as they need to be described during bubbling for practical application, are explained by the π-theorem or the experimental design method. A summary of theoretical and experimental data for determining the calculating parameters of bubbling degassers let us conclude that using the diffusion coefficient is inappropriate. In the absence of data on the desorption coefficient, we recommended to use the water-air ratio and the contact time, depending on the expected effect of carbon dioxide removal, as determining parameters for calculation.
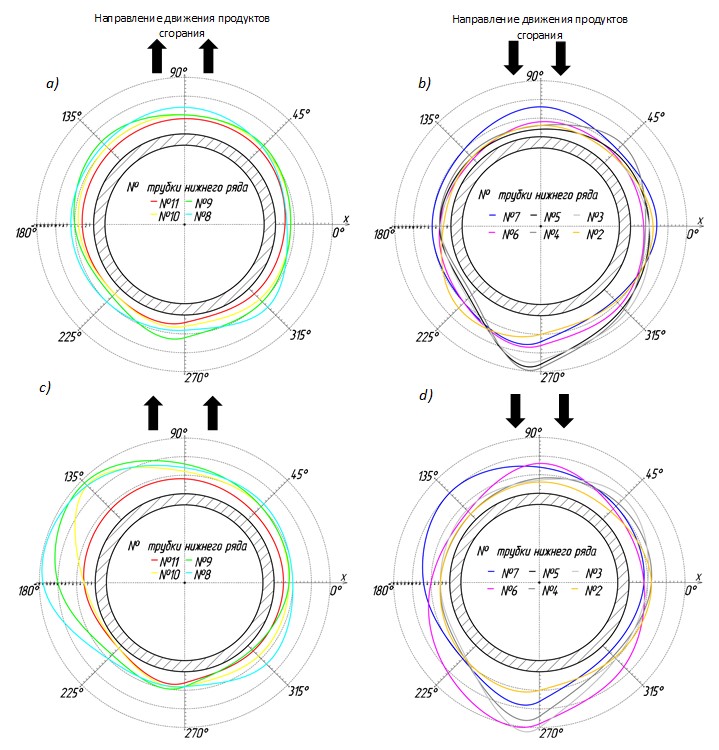
This study presents the results of an investigation into the state of ash deposits on the surface of circular cross-section pipes in the convective sections of two hot-water heating boilers, model KVu-1.0 (manufactured by Baltkotlomash LLC, St. Petersburg), each with a thermal capacity of 1.0 MW. The boilers were operating on long-flame coal with a granulometric composition of 20–50 mm. The physical properties of the ash deposits and the factors influencing their formation on the pipe surface during boiler operation are briefly described. Based on the results of in-situ measurements of deposits formed during the 2023–2024 heating season, the growth of tube ash deposits was analyzed. The shape of the ash deposits is presented through graphs depicting their cross-sectional projection on convective tubes with a diameter of 48 mm.
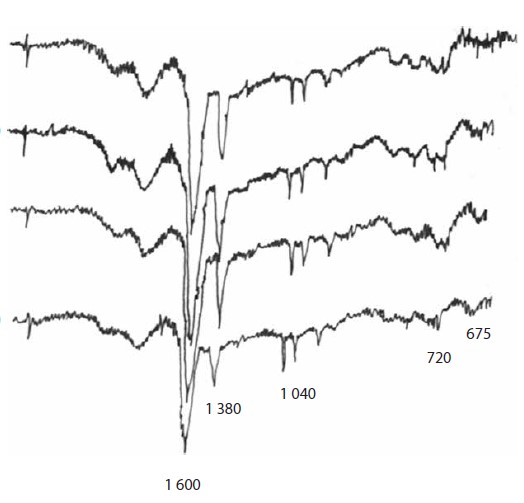
The use of electric steelmaking slag in road construction allows decreasing the cost of the produced products, and solves an important environmental problem by reducing the areas occupied by dumps. In laboratory conditions, recipes for using the electric steelmaking slags as crushed stone, sand, and mineral powder for asphalt concrete are most often developed without taking into account the effect of shelf life in dumps on the properties of slag materials. During the long-term storage of slag, its phase composition changes, so the use of mineral powder based on electric steelmaking slag of current output and slag stored in dumps for more than 5 years requires preliminary analysis of its properties. IR spectra of bitumen were recorded after their interaction with mineral materials based on electric steelmaking slags of various shelf life in dumps. The physical and mechanical characteristics of asphalt concrete were examined with the introduction of slag mineral powder into its composition, and recommendations were provided for using electric steelmaking slags in road construction, taking into account the aging processes occurring during the slag storage in dumps. According to IR spectroscopy, the storage time of slag in dumps does not significantly affect the diffusion of bitumen light fractions into the pores of the slag mineral material. When using electric steelmaking slag as a mineral powder for asphalt concrete, current-output slag and slag stored in dumps for several years behave similarly. The most effective approach is to use current-output slag as a mineral powder.
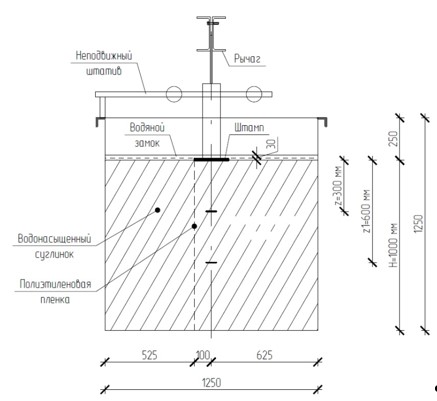
When designing buildings and structures on soft water-saturated soils, it is necessary to calculate the stress-strain state of the foundation with creep. This allows us to predict the development of deformations over time, redistribute creep-induced forces to improve the reliability and durability of structures, and helps reduce the risk of emergencies. This study calculated the stress-strain state of a viscoelastic foundation using a kinematic soil model within the framework of the linear hereditary theory of viscoelasticity. Experimental graphs of pore pressure changes and stamp settlement were presented as time functions using broken-line method by L. E. Maltsev. All results are illustrated by graphs. A methodology for obtaining the original function from a transform is shown. Mechanical viscoelastic characteristics were determined according to the kinematic soil model. Using the obtained data, it is possible in the future to determine the development of settlement over time for viscoelastic water-saturated foundations.
TRANSPORT
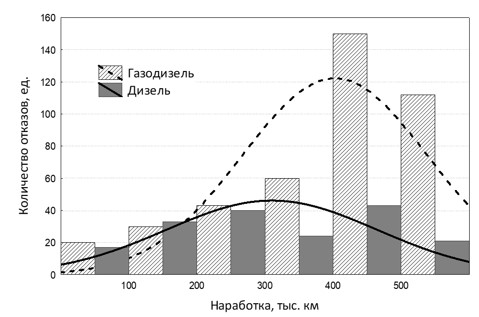
Based on proven statistical data, the experience of operating gas-powered vehicles was analyzed using the example of gas-diesel modifications of KAMAZ truck tractors, taking into account actual reliability, design features of the fuel system, and load capacity. The analysis of the cargo transportation tasks frequency was conducted based on waybills and approved schedules for construction and installation work for the maintenance of gas transportation infrastructure facilities. It also included an assessment of maintenance costs and formalization of criteria for optimizing transport routes. During the comparative analysis of tractor trucks with conventional and gas-powered engines, new patterns of transportation cost formation were established and a multi-criteria efficiency assessment system was developed. This system takes into account economic, operational, and logistical parameters. For practical application of the obtained results, a mixed-effects model with a single-step function was proposed. The use of this model makes it possible to reduce the transportation costs by 18% by increasing the fleet utilization rate and optimizing logistics routes for cargo delivery at the facilities of the gas transmission system.
Effective management of the service station’s production area load is a key factor in improving customer service quality and operational efficiency. The proposed approach to optimizing vehicle distribution among service stations is based on scheduling theory and takes into account station specialization, customer priorities, and waiting time minimization. A dynamic task assignment algorithm, implemented in Python, is developed using a greedy strategy focused on early resource release. A software application with a web interface and a schedule visualization module has been created for practical application. This software product may be of interest to automotive and specialized equipment service companies for managing service station loads. The proposed approach provides a balance between computational efficiency and schedule quality, making it suitable for real-world application in urban service stations.
ISSN 2713-0770 (Online)