ARCHITECTURE
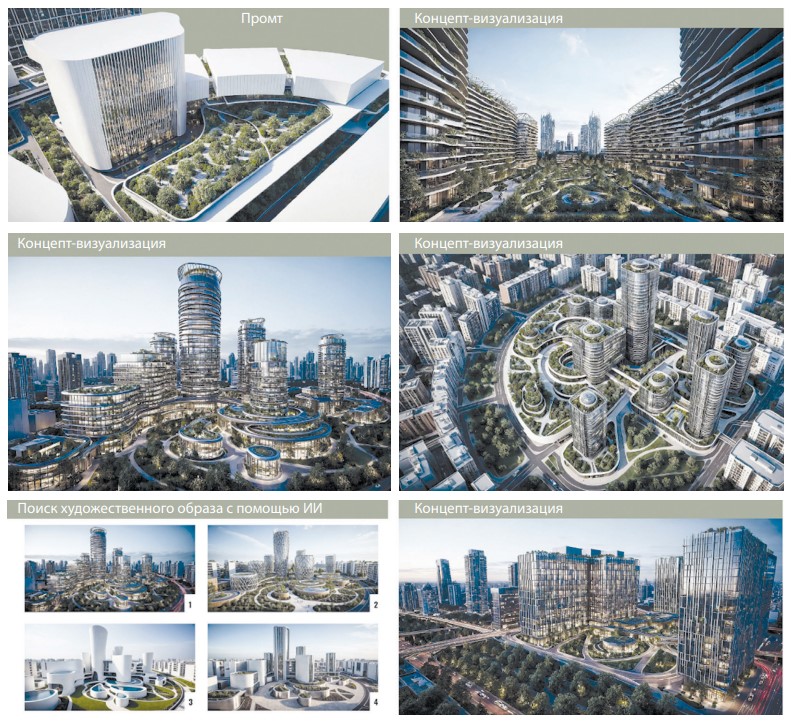
This article addresses the issue of integrating artificial intelligence into curricula and programs in the "Architecture" specialty. Al is considered as an essence of modern creative work and is analyzed as an integrative model in terms of its positive and negative aspects for training future specialists. Since the architectural profession is heavily influenced by technological advancements, including AI, architectural education, which largely preserves the traditions of the classical school, must develop a new systemic approach to integrating these innovations into the educational process. The study analyzes contemporary methods for integrating AI into the architectural education of Russian universities (Moscow Architectural Institute (State Academy), Nizhny Novgorod State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Ural State University of Architecture and Art, Novosibirsk State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering (Sibstrin)). It also presents practical experiences of students, graduates, and lecturers from the Department of Architectural Environment Design at the Industrial University of Tyumen. The research revealed that in the absence of a methodological framework for integrating AI into architectural education, studying these technologies is becoming a necessary condition for the professional training of modern specialists. The authors propose a conceptual model for phased integration, based on the principles of cultural continuity, progressive complexity, and critical reflection.
CONSTRUCTION
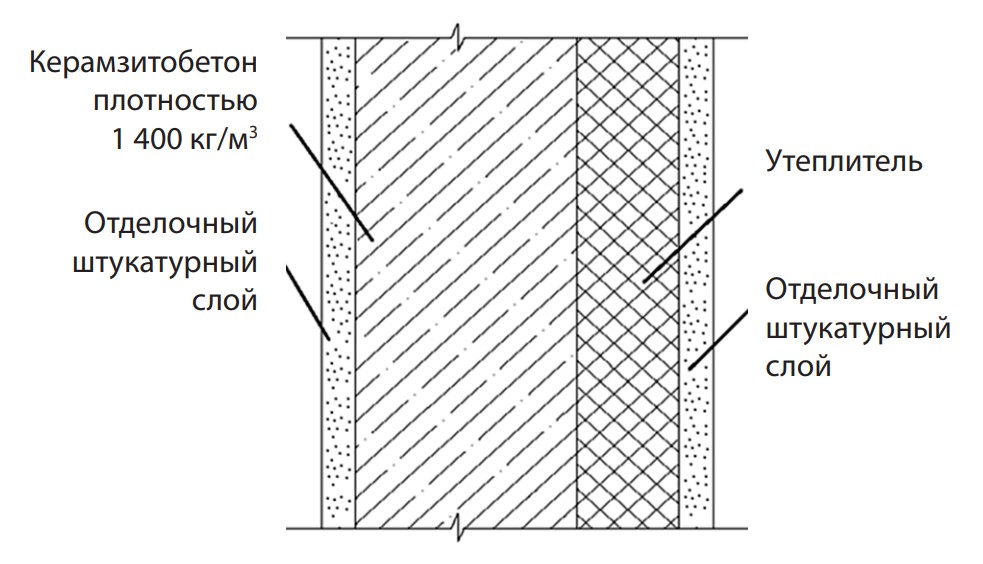
This study investigates the influence of plaster coating based on a developed dry mix containing synthesized aluminosilicates on the thermal and moisture regime of building envelopes under various operating conditions in the cities of Novosibirsk and Penza. Two finishing options were analyzed during the calculations: the first used a lime-sand mortar with a density of 1.600 kg/m3 for finishing both interior and exterior surfaces, while the second used the same mortar for the interior finishing but employed a plaster mix with a density of 700 kg/m3 based on the developed formulation for the exterior. The results obtained suggested that the developed thermal insulation plaster was effective in the climatic conditions of both cities. It ensured faster drying of the wall structure compared to cement-sand mortars, and a 1.6–3 mm shift of the zero isotherm towards lower temperatures was observed. Furthermore, using the plaster based on the developed formulation reduced the amount of condensation within the wall structure by a factor of 19.4 in Novosibirsk and almost completely eliminated it in Penza. The moisture content of the material was 4.7 times lower in Novosibirsk and 3.2 times lower in Penza compared to lime-sand analogues. This indicates an increase in the thermal insulation properties of the external building envelope.
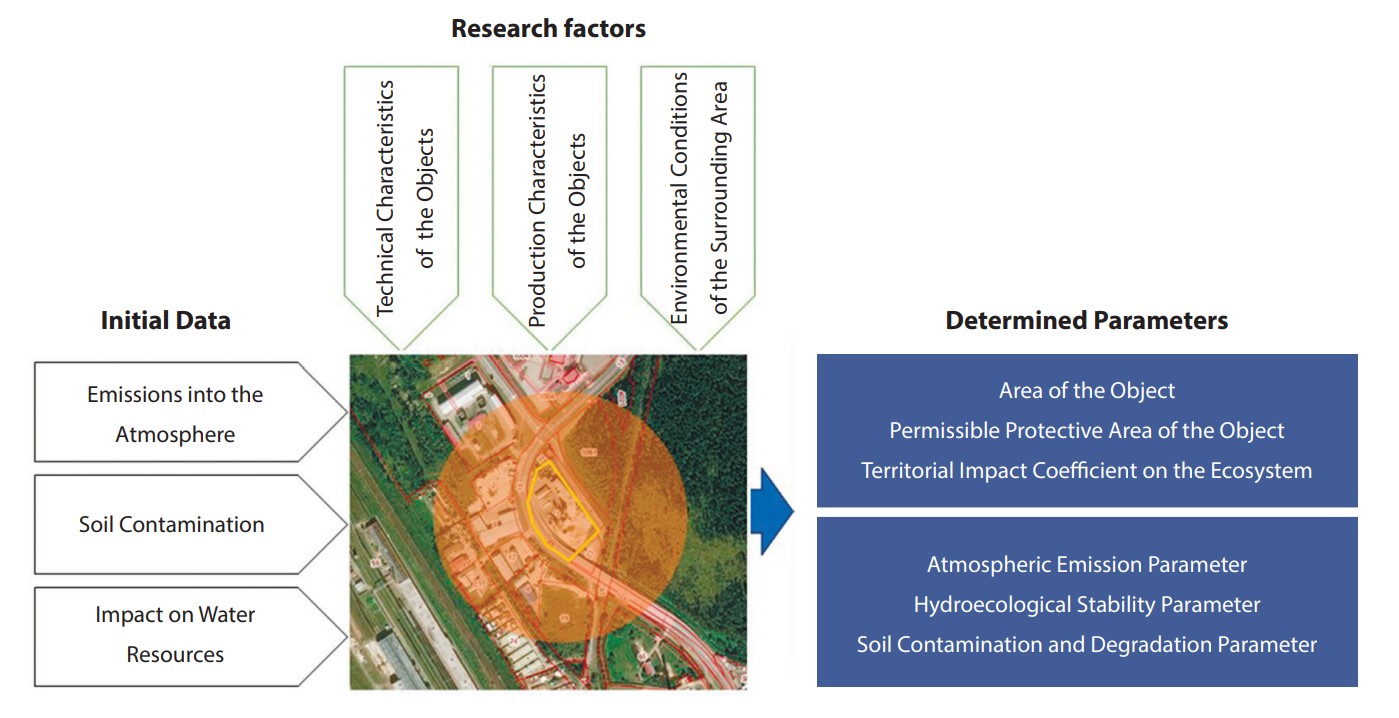
The study addresses the environmental risks posed by asphalt concrete plants operating in industrial zones, focusing on their impact on air, soil, and water resources. The objective was to develop and test an integrated criteria-based methodology for assessing such impacts. Three asphalt concrete plants with different production capacities and gas-cleaning efficiencies were selected as the research objects. The methodology included sequential evaluation in five areas: territorial impact, geological conditions, atmospheric emissions, soil degradation, and water pollution. Data collection involved satellite imagery, cadastral surveys, laboratory analyses of air and soil samples, and field observations. The results show that plants with higher production capacity generate significantly greater environmental loads, with CO2 and NOx emissions exceeding permissible levels, and with notable soil degradation and risks to hydrogeological stability. The discussion highlights that upgrading gas-cleaning units, implementing continuous water quality monitoring, and restoring disturbed soils are essential to mitigate the negative impacts. The proposed methodology proved effective for comprehensive environmental risk assessment and can be applied to other industrial facilities with similar environmental profiles.
This study provides an inductive analysis of current normative and technical documentation for geotechnical monitoring. Based on it, the main disagreements and inaccuracies were identified and measures to eliminate them were proposed. During the study, 26 current normative documents were analyzed through 32 criteria. Initially, it was determined whether these documents were included in the List of National Standards and Codes of Practice, which directly affects the obligation to comply with the document requirements. Documents without concrete requirements to monitoring or with limited range of application were excluded from further analysis. The subsequent analysis was carried out according to criteria such as the timing and cyclicity of work; the location of the source and survey points, and their quantity; the accuracy of determining the position of the points; special instructions when working on landslides, etc. As a result, significant differences have been identified among normative and technical documents governing geotechnical monitoring of landslide processes, specifically in their requirements for the timing and cyclicity of work (they range from 1 day to six months). Furthermore, there is no reliable list of controlled parameters that would be identical for several documents. The following research areas have been identified: developing a system of dependencies of the limit values for controlled parameters; standardizing the optimal number of points depending on the scale of landslide phenomena and topographic conditions of work.
TRANSPORT
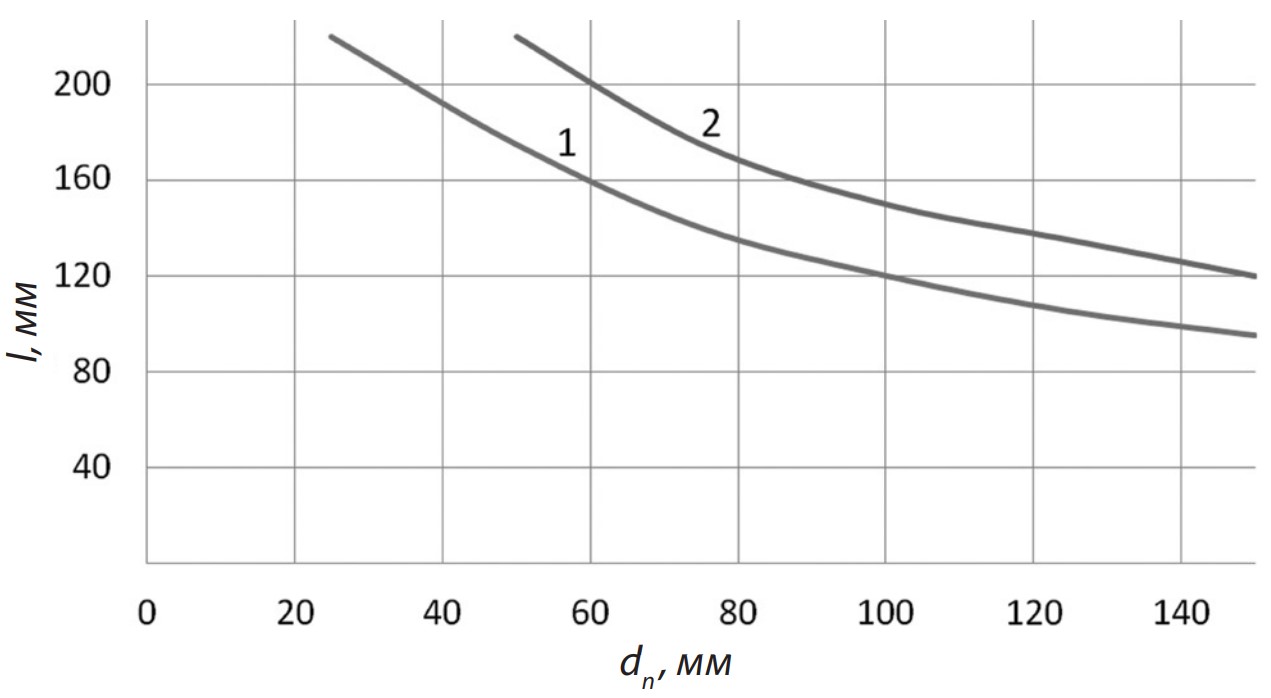
One of the most effective methods of developing high-strength soils, including frozen soils, is impact destruction using active-type mechanisms. In this case, the most appropriate application is using impact devices as independent replaceable or modernized loading and unloading equipment for base machines, for example, for excavators with hydraulic drive. The key advantage is the ability to perform a full cycle of work: from the destruction of solid or frozen soil to its direct loading into vehicles or dumps without changing the working implement. After analyzing existing bucket types, we developed an active-type bucket, which was considered to be the design of a hydraulic-pneumatic impact mechanism for loading and unloading equipment. Defined technical specifications of a hydraulic-pneumatic impact mechanism for an active-type bucket take into account both the requirements for the destruction process and the soil loading efficiency. The study presents calculated dependences for determining the main parameters of the pneumatic accumulator of the hydraulic impact mechanism. The most important of these are striker mass, impact energy, gas pressure, and charging pressure. These parameters are necessary to ensure the required impact energy during excavation and reliable operation of the device during the loading cycle. Graphs were presented showing the correlation between pneumatic accumulator length and diameter, and the dependence of pneumatic accumulator energy on charging pressure.
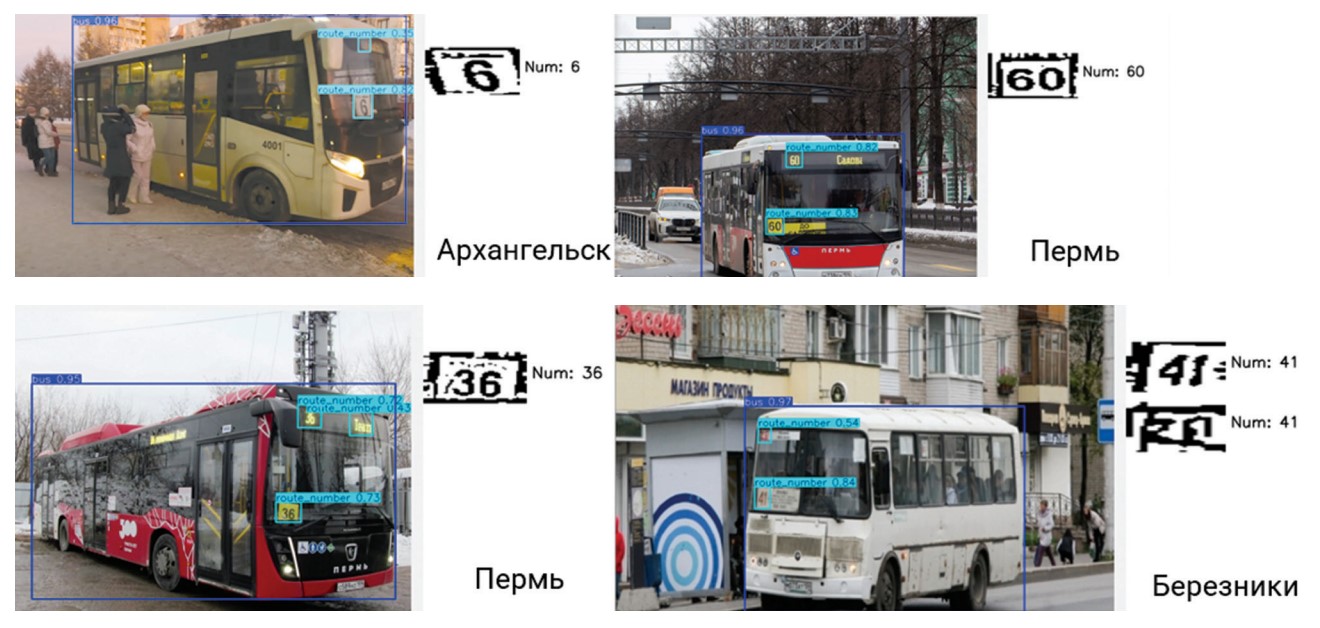
This study focuses on developing software to address a practically important problem: providing public oversight of urban transport movement. This is particularly crucial in areas with limited GPS/GLONASS and cellular connectivity. The core of the system comprises video cameras located along the route and a computer vision system. This system detects the presence of buses or trolleybuses in the camera’s field of view, localizes them, and recognizes their route numbers. Using the freely available YOLOv11s object detector, a machine recognition accuracy of 96 % was achieved. This version of YOLO is resource-efficient, enabling the use of a standard personal computer to process multiple video streams. Route numbers were recognized using the open-source PaddleOCR library, achieving an accuracy of 82 %. The obtained results were compared with the bus schedule, and the data was posted via a Telegram bot. The research results aim to improve the convenience of urban public transport, reduce social tension, and provide residents and dispatching services with real-time information about deviations in urban transport operations.
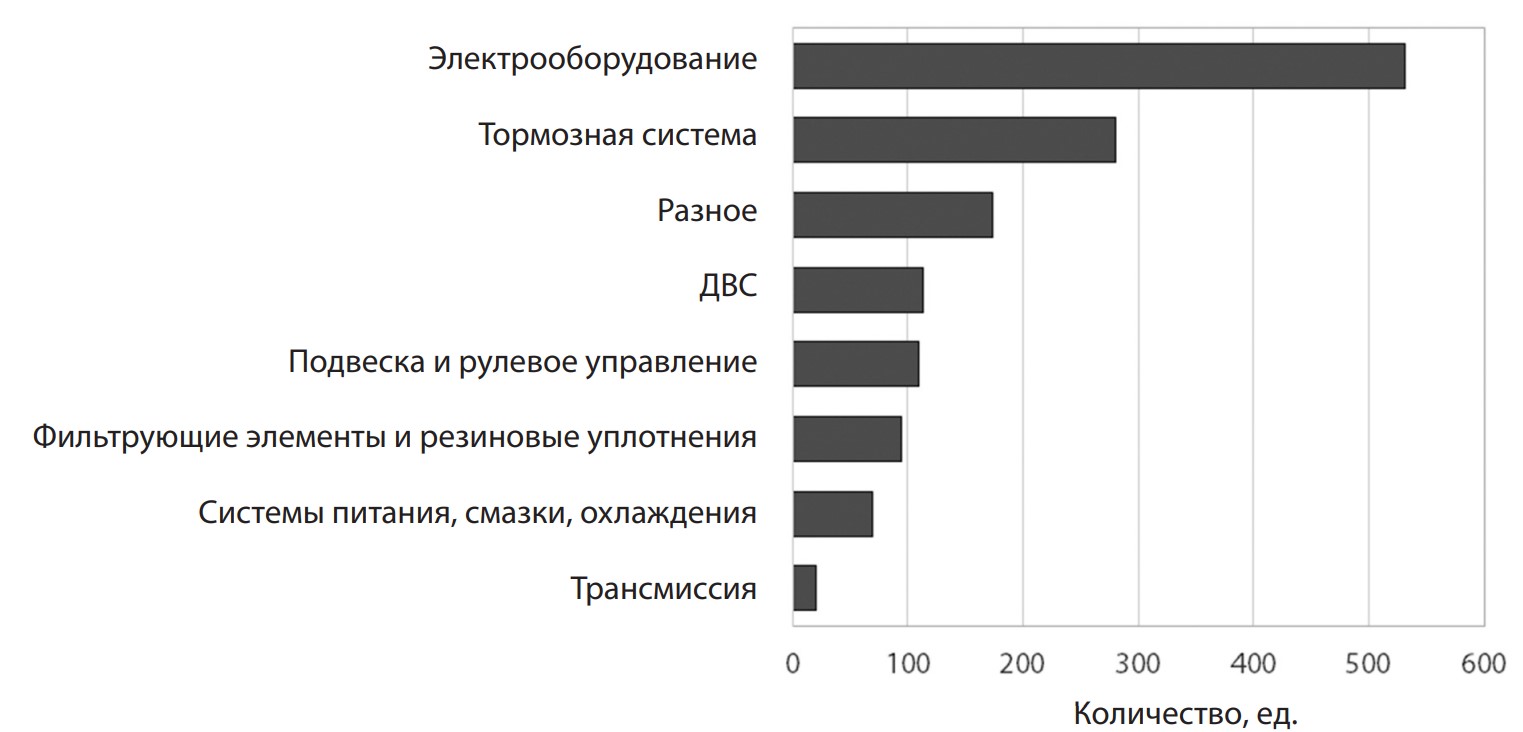
The cost associated with the procurement and storage of spare parts accounts for almost a third of the overall structure of automotive transport operating expenses. Consequently, inventory management is a crucial aspect of enterprise operations, and research focused on developing more accurate methods for predicting the need for spare parts is of practical interest. This study proposes planning spare parts inventory based on their reliability. The essence of this approach is dividing spare parts into groups according to their failure rate and further determining the quantitative and nomenclature needs within these group. The study was conducted using KAMAZ-54901 vehicles. In accordance with the vehicle’s design, spare parts were divided into 8 groups. Statistical data revealed groups of spare parts with low reliability (electrical equipment, braking system). Therefore, these groups will necessitate the largest stock volumes. This approach enables the optimization of spare parts stock at the enterprise's warehouse.
ISSN 2713-0770 (Online)