ARCHITECTURE
Creating inclusive educational environments in schools is a pressing issue today, yet its practical implementation remains limited to a few schools. This work draws upon a review of Russian and international theoretical literature outlining the requirements and recommendations regarding architectural space, design, functional relationships, and the typology of specialized classrooms for educating children with ASD. Considering these requirements, the authors analyzed the architectural-environmental, spatial-planning, and functional-technological solutions for implementing an inclusive educational environment, as piloted at School No. 96 "Eureka-Development named after Nagibin M. V." (Rostov-on-Don). The advantages identified include: the availability of multiple classrooms capable of accommodating over 40 children; the multipurpose use of spaces; the use of both specialized and standard furniture and equipment; the integration of environmental elements to support special education needs (therapeutic pedagogy) within the classroom structure; and the possibility of holding inclusive events in school-wide facilities. Disadvantages identified include the lack of several essential rooms; the division of the inclusive unit across two floors; compromised classroom functionality due to reduced floor space per student; and unclear functional zoning within classrooms. Based on the literature reviewed, the following improved spatial planning solutions were proposed: creating a dedicated resource area featuring a broader range of specialized classrooms and support spaces; locating the entire inclusive unit on the ground floor; reorganizing the school’s entrance area; installing an elevator to facilitate access for individuals with limited mobility; and considering the addition of an integrated, attached building unit.
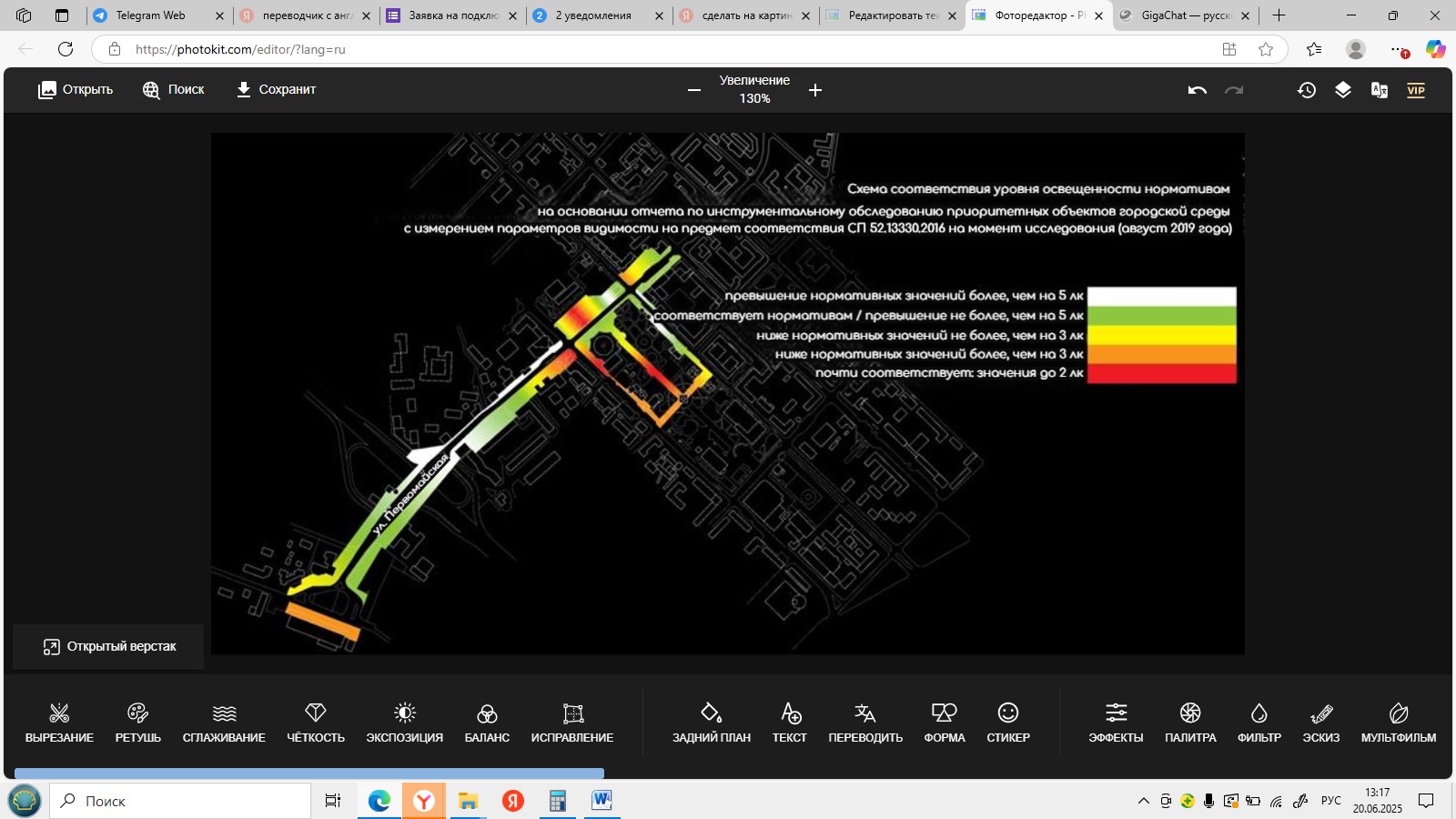
Modern light projections and holographic technologies represent promising tools for the qualitative transformation of the urban environment, creating unique architectural images, and improving experience in urban spaces. Analysis of Pervomayskaya Street, one of the central thoroughfare in Tyumen, revealed several issues related to its lighting design: uneven illumination, low efficiency of existing lighting fixtures, a lack of adaptive lighting modes to accommodate seasonal and diurnal changes, as well as insufficiently developed scenarios for architectural features and green spaces. To address these shortcomings, comprehensive measures have been proposed to improve the street’s lighting scheme, focusing on enhancing comfort and safety within the urban environment and fostering a positive psychological atmosphere. Proposed solutions include employing projection lighting to illuminate shadowed sections of the pedestrian zone and light projections to enhance abandoned objects and vacant lots, designing dynamic illuminated facades that adapt the visual appearance of buildings based on various factors and serve as supplementary lighting during nighttime hours. The integration of innovative approaches into the urban planning process unlocks the potential for creating a next-generation comfortable urban environment.
The relevance of this research stems from the need to revise the content of urban planning standards for cities in Western Siberia. The focus of the study was the residential development plot as an object of urban planning regulation. The authors considered 60 residential plots in Tyumen and Omsk (30 in each city) developed between 2009 and 2019. The study aimed to identify the mutual influence of land plot size, open space morphology, and planning characteristics on the type of land development. The application of factor and cluster analyses facilitated the identification of the underlying structure within the raw data, relevant to the context of design decision-making. Factor analysis was used to group the variables from the initial dataset into a two-factor model: the first factor comprised planning indicators, and the second – morphological characteristics. Cluster analysis enabled the classification of objects based both on the variables used in the factor analysis and on the urban planning indicators employed for evaluating the design solution.
CONSTRUCTION
Designing buildings and structures on weak, water-saturated clay foundations necessitates calculating the stress-strain state of soils over time, considering consolidation processes. These soils exhibit creep behavior, respectively, making a viscoelastic representation of the foundation a promising modeling approach. Numerical analysis identified a parameter for solving the transcendental equation of a nonmonotonic function that describes the viscoelastic mechanical properties of the water-saturated clay loam. Experimental pore pressure data were compared with data obtained from the solution of the time function, with a maximum discrepancy of 4.44 per cent. A mechanical characteristic (a universal parameter of the kinematic soil model) obtained in this study can be used in future to fully calculate the stress-strain state of viscoelastic, water-saturated foudations. The proposed approach undoubtedly holds practical value in the design and construction of engineering structures.
Implementing economically viable energy-saving measures is a priority for any large enterprises.
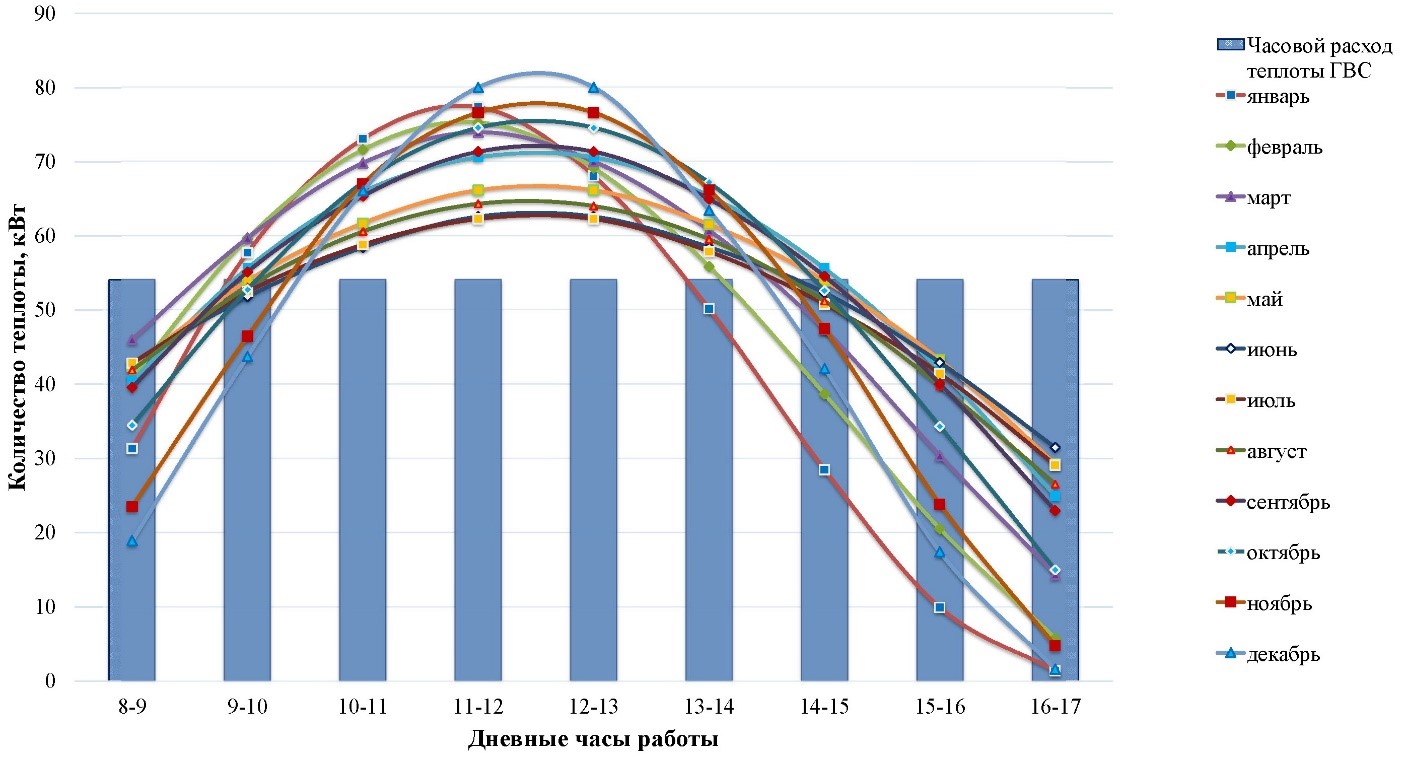
Hot water supply system as one of the major heat consumers in airports offer significant potential for energy consumption reduction. Electric boilers are the primary heat source for the hot water system of the Vladivostok airport. To reduce energy consumption, the application of solar collectors for water heating and the installation of exhaust air heat recovery systems were considered. To evaluate the effectiveness of these energy-saving measures for the airport’s hot water system, theoretical calculations of water and heat consumption for domestic hot water were performed, and these were compared with actual values obtained from heat meter data. Based on these data, the actual average daily hot water consumption over 4 months was 6.68 m3/day, with an average passenger flow of 258 passengers per hour. The theoretical consumption for the same passenger flow was 6.83 m3/day. At a design passengers flow of 1.360 people per hour, the average daily water consumption was calculated to be 13.92 m3/day. The study calculated the key indicators of implementing the energy-saving measures at the design value of passenger flow. Supplying domestic hot water using exhaust air heat recovery has a simple payback period of 6.81 years; a payback period of solar hot water system comprising 86 solar collectors is 11.2 years.
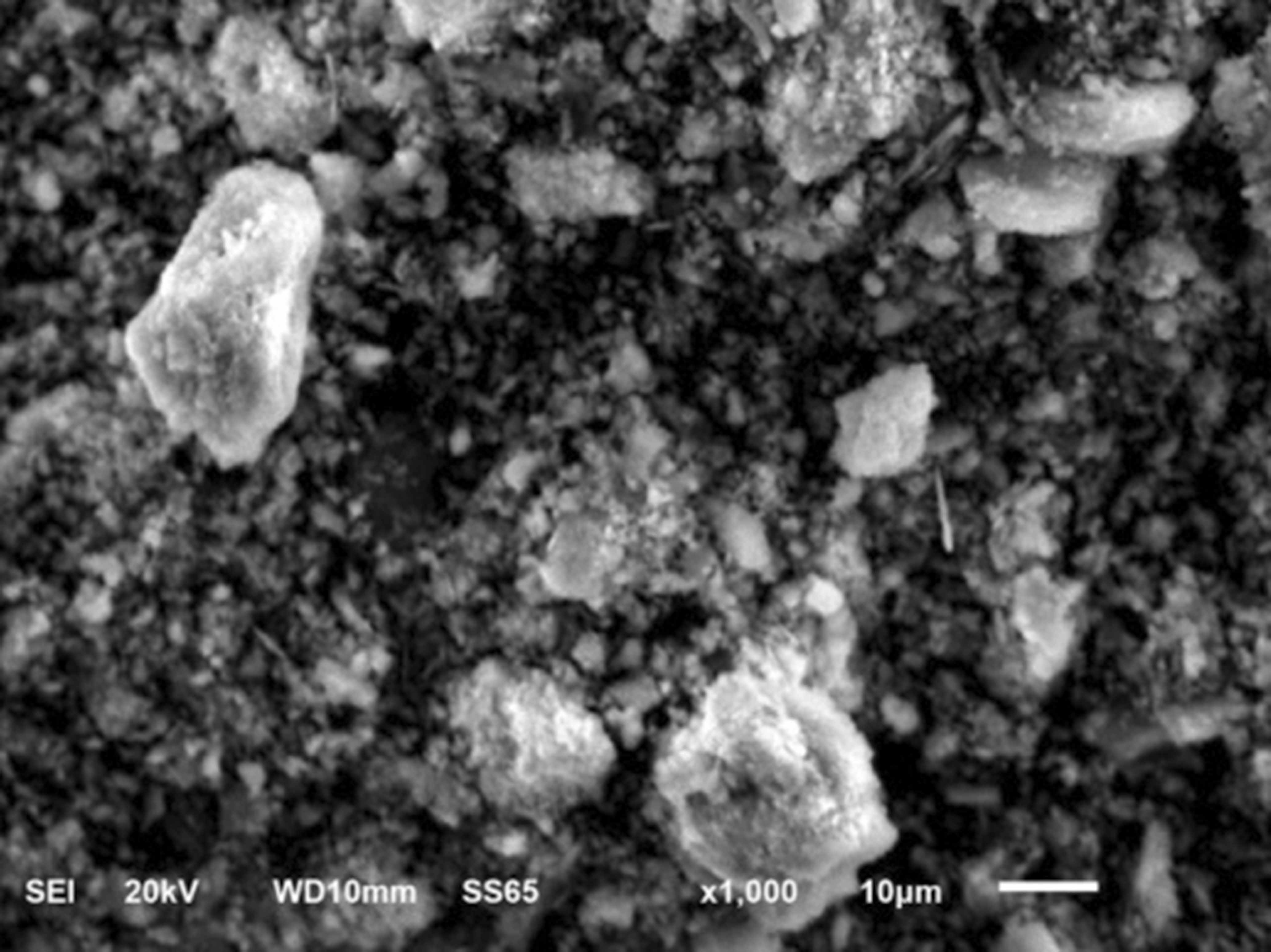
Plastic can be recycling in three ways: chemical, thermal, and mechanical. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages. The most prevalent is mechanical processing, resulting in recycled materials or composite materials. A key objective in producing composite materials through this method is to restore or enhance their properties using modifiers. The properties of these additives depend on the shape and size of their particles. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy was used to determine the elemental chemical composition of a plasticizer based on highly dispersed calcium hydroxide. X-ray diffraction analysis performed on a DRON-7 diffractometer made it possible to identify the chemical compounds within the additive. Scanning electron microscopy was employed to determine the shape and size of the particles. The optimal result, specifically a four-fold reduction in stiffness, was achieved using spherical particles with a size range of 0.5–1 μm.
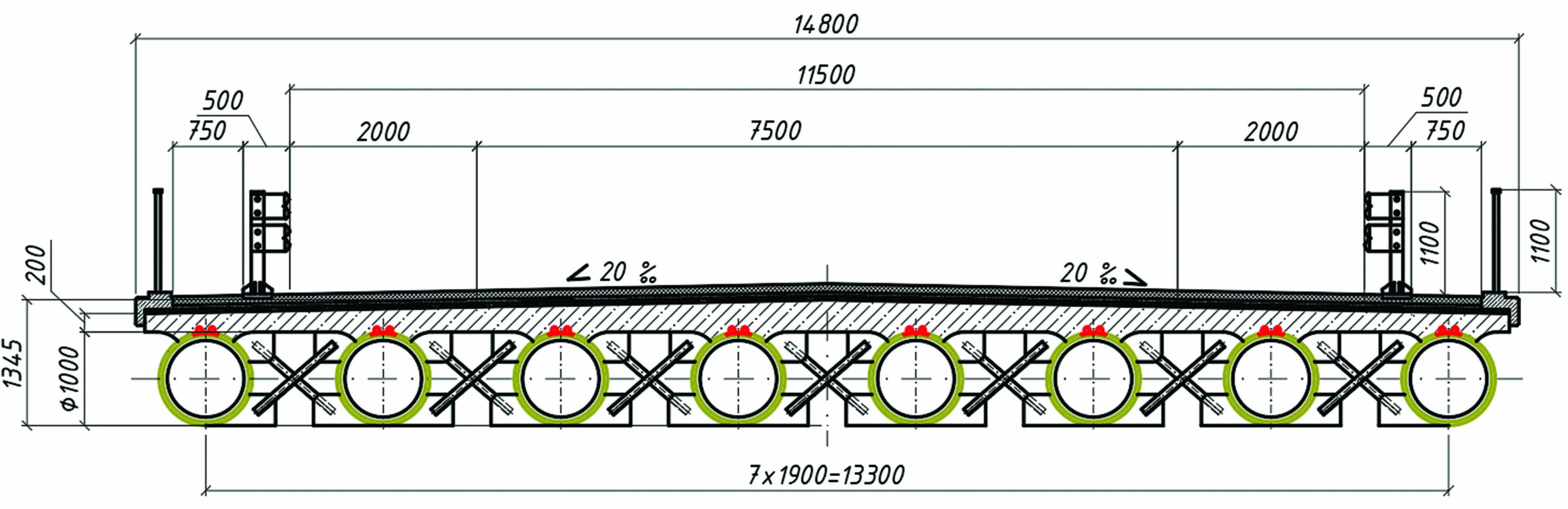
The study is aimed to increase durability and reduce costs in bridge construction through the use of fiberglass pipes manufactured by the filament winding process. Despite the successful use of fiber reinforced polymers (FRP) abroad, their application in Russia is limited due to the lack of regulatory framework and insufficient study of their mechanical properties. Through experimental tensile testing of fiberglass pipe specimens using strain gauges and a universal testing machine, key characteristics were obtained: tensile strength (200 MPa on average), elastic modulus (29.5–37.9 GPa), and Poisson's ratio (0.21–0.27). The material properties were found to be comparable to concrete and steel, which confirms its suitability for hybrid bridge superstructures. The peculiarities of the deformation behavior, including cracking and changes in the elastic modulus under repeated loading were revealed. The results of the study can be used to develop a regulatory framework and to design durable bridge structures, opening up perspectives for the expansion of composite applications in construction.
TRANSPORT
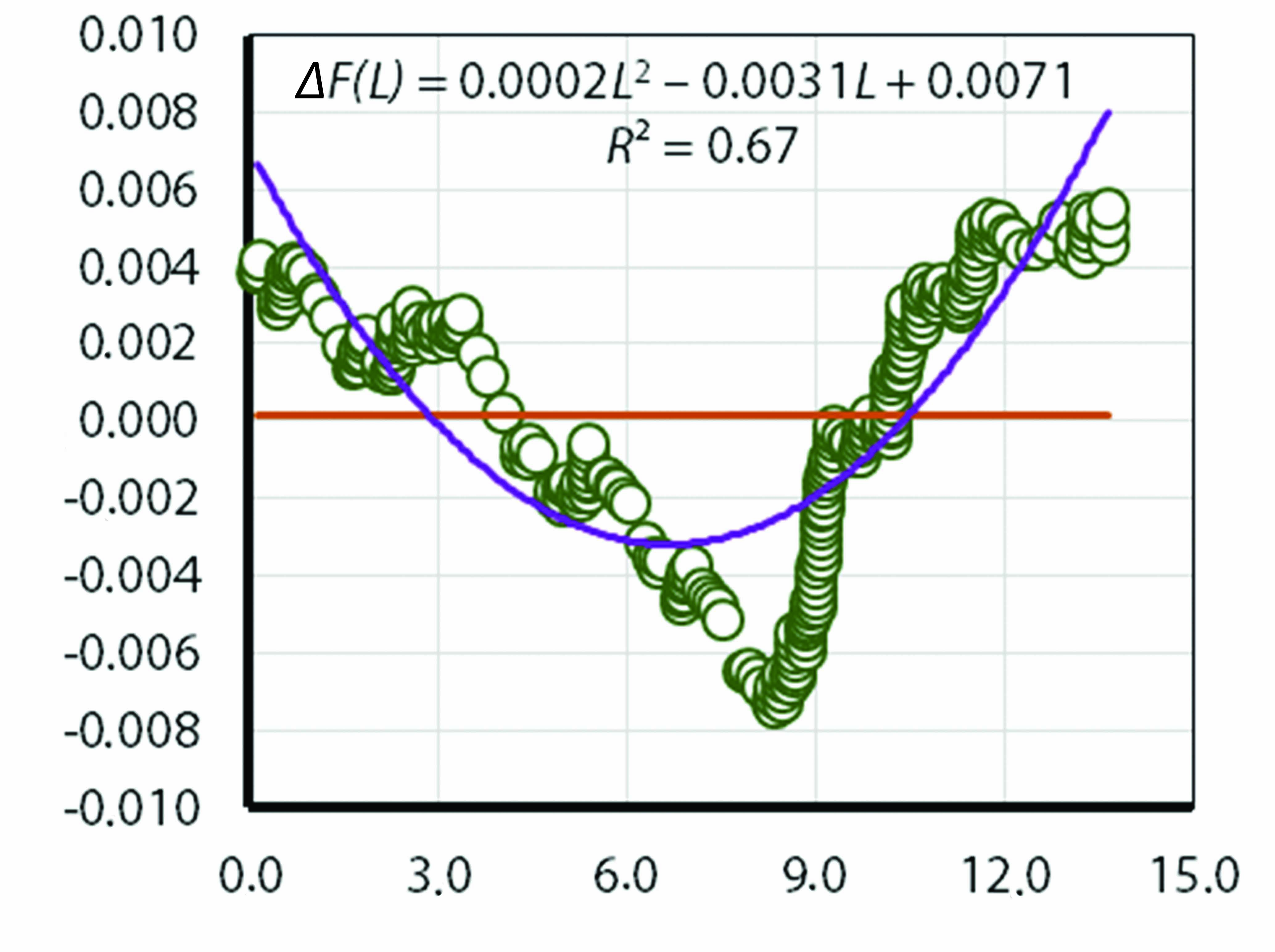
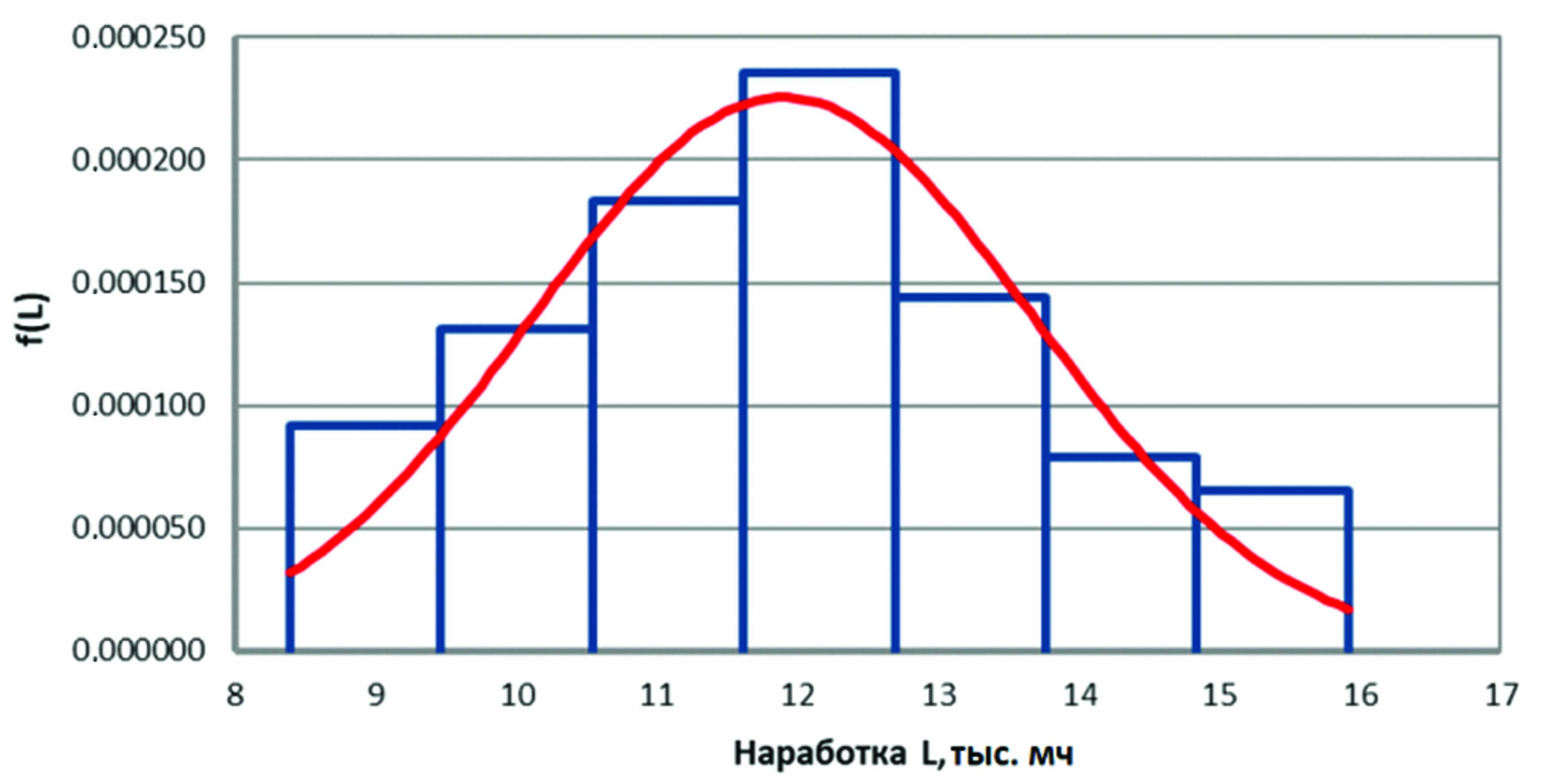
Motor transport enterprises often conduct maintenance of vehicles under warranty service using their own facilities. Due to the influence of various factors, the actual operating time between maintenance operations often deviates significantly from the normative ones. Existing methods do not allow accurately determining the change in failure probability for a vehicle group, because the actual operating time at the completion of the maintenance cycle is a stochastic value. This paper proposes a method for evaluating vehicle maintenance quality, based on the ratio of failure probability increments before and after maintenance, taking into account the specific operational characteristics of the vehicles. The research employs an axiomatic method: the failure rate decreases after maintenance and increases with accumulated operating time. The research hypothesis posits that maintenance quality can be assessed by the ratio of failure probability densities in sections before and after maintenance (first section: operating time 0 to 7.5 thousand km; second section: operating time 7.5 to 15.0 thousand km). Data on vehicle failures during actual maintenance intervals were collected and processed for two structural divisions of a city-forming enterprise in Surgut. The developed mathematical models are statistically significant with a probability of 0.99. The resulting values of the developed quality indicator – 1.947 for the first enterprise and 1.731 for the second enterprise – indicate that the system for ensuring the operational reliability of the investigated enterprises is effectively organized. Further work is planned to evaluate the maintenance quality across different car brands to obtain a broader spectrum of values and facilitate their subsequent interpretation.
The service life of thermal engines in transportation and transport-technology machinery determines the efficiency of a wide range of technological operations. Therefore, ensuring high-quality maintenance, considering the operating conditions and intensity of use, is a critical task. This research focuses on analyzing ten years of experience with internal combustion engines in transport divisions of oil and gas production companies. Using the YaMZ-238 engine as an example, it is shown that one of the primary reasons for the reduced mileage before overhaul is untimely maintenance, where the coefficient of variation in maintenance frequency exceeds 0.5. Reducing this value to 0.1 increases the integrated operational reliability and the technical readiness rate of the vehicle fleet by 15 per cent. Consequently, the potential reliability of the engines can be realized through a comprehensive set of measures designed to improve the organization of the maintenance system within the transport divisions of oil and gas production companies.
ISSN 2713-0770 (Online)