ARCHITECTURE
Colour plays an important role in creating a safe and informative urban environment. However, there is still a tendency towards colour monotony or, on the contrary, chaotic flashy colours in the colourism of urban space. The globalisation process in urban planning also has a negative impact and leads to the loss of individual image and recognition of modern fast-growing cities, including Tyumen. The article studies the colouristics of the city, its formation under the influence of colour culture and colour preferences of citizens. The author compares the existing methods of formation of urban environment colouristics based on a set of different factors. A special place in the study is given to regional colour culture. Its basis lies in the colour preferences of a person, certain social groups or a nation. The study of the history of colour culture in Tyumen relies on historical and qualitative methods, analysis of archival materials, various written and visual documents. The study gives examples of the influence of colour culture on the formation of urban environment colourism. Field surveys of real architectural objects in the central part of Tyumen and the analysis of changes in colour preferences caused by the change of colour carriers made it possible to identify the colouristics peculiarities in the city in certain periods of its construction. Scientific novelty consists in an in-depth consideration of the formation of urban environment colouristics in the context of regional colour culture.
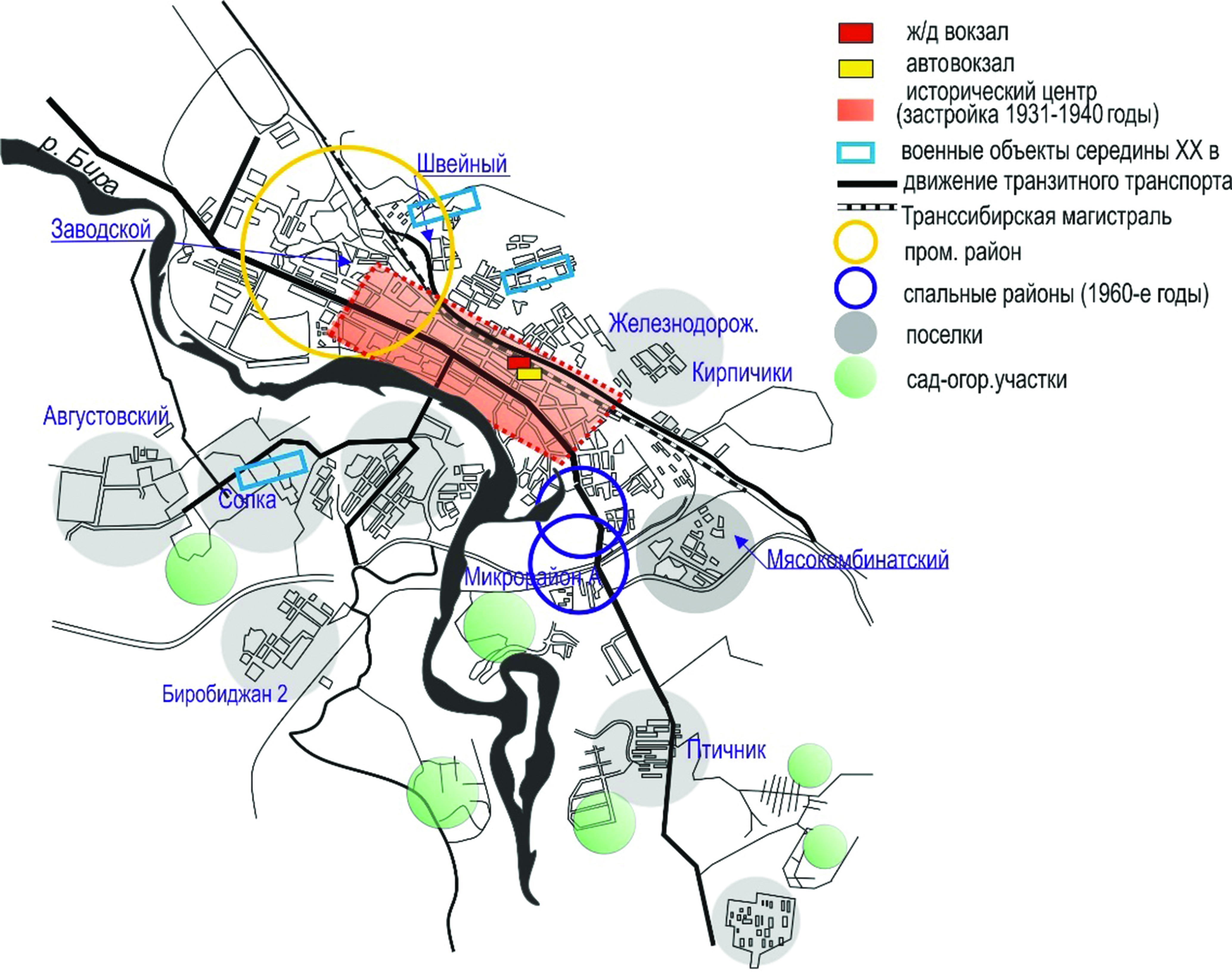
A number of studies are devoted to the urban development of settlements in the Far East, but they do not consider trade spaces as structureforming spaces, whereas they often form the framework of the city. After studying the cadastral maps of Birobidzhan, topographic survey materials, online maps and other documents, we identified five historical periods of formation of outdoor trade spaces in Birobidzhan and their architectural and planning features. The first stage was 1928-1933: the period of free development of the territory, when the trade environment was an instrument of social adaptation of the developed space. The second was 1932-1937, when professional architects were invited to the planning and development of the city, and the market square received its official status. The third stage was 1937-1990: the period of planned development of the territory, when the planned trade environment was formed. The fourth was in the 1990s: it was the time of post-socialist transformation, the typical feature of which was self-organization of market space, the trade street reflected the crisis phenomena in the urban system. The fifth stage lasts from 2000 to the present and includes reorganization of trade spaces: demolition of old pavilions and stalls in the Central Market area, emergence of seasonal fairs as a new form of open trade in the city, concentration of small open trade spaces near the existing markets at the same time with separate functioning of large shopping centres that close the adjacent territories from street trade. The comprehensive programme for the implementation of the concept "Compact competitive city with jewish colour on the border with China" (master plan of Birobidzhan until 2030) envisages, among other things, the renovation of trade spaces. It should take into account trade as a social phenomenon.
CONSTRUCTION
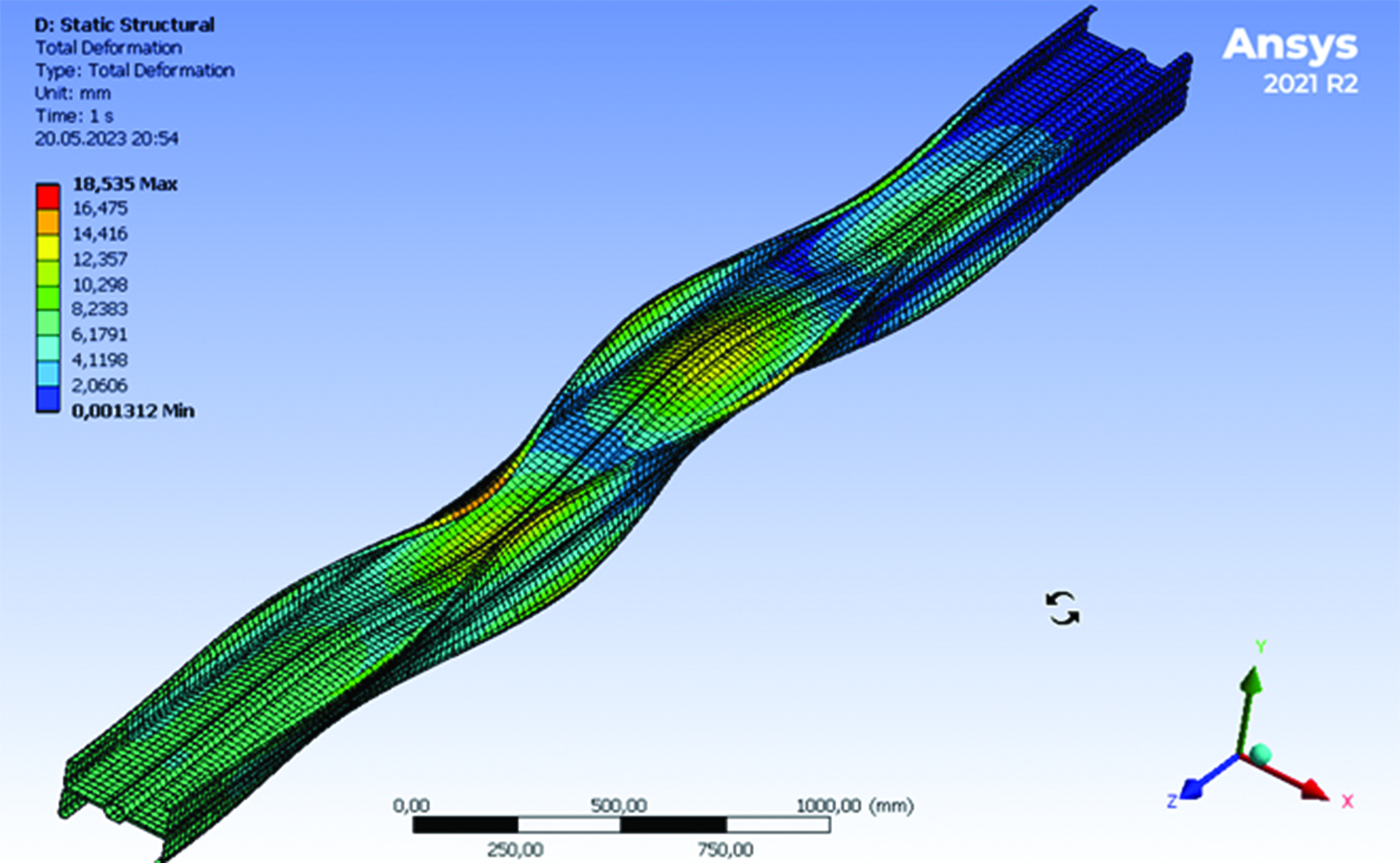
Despite the increase in the growth rate of construction with the use of steel thin-walled sections, the building code for the design and calculation of these structures has a number of conventions and indicates the preferred use of the results of experimental studies in the design. Full-scale tests are generally not available during design, so numerical modelling is a correct alternative. The analysis of existing scientific literature shows that there is no consensus among researchers regarding the main parameters of the models and the modelling algorithm in general, so the aim of the paper is to develop recommendations for modelling thin-walled sections. The results of the study for object made from a coupled sigma profile under axial compressive force conditions let us develop key recommendations for modelling including the use of finite element type, finite element mesh parameters, the mechanism of application of boundary conditions, external loads and other model parameters. The results were verified by analytical methods of thin-walled sections calculation. The obtained convergence of the results indicates the possibility of using these recommendations in the design and calculation of thin-walled structures.
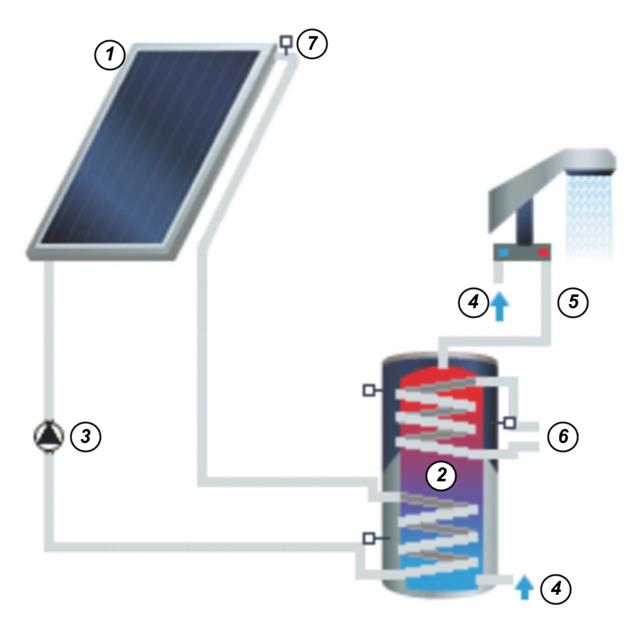
The hot water supply system of Perm uses solar energy. The aim of the study was to substantiate the economic efficiency of solar collectors and determine their payback period taking into account climatic conditions, equipment cost and economic criteria. The proposed technical solutions of solar energy using were analyzed and compared with electric heating. During the study, the authors defined the required minimum solar collector area for a household (taking into account the hot water standard for Perm) as a functional dependence of the amount of incoming solar insolation on the amount of using heat energy. We evaluated domestic and imported solar collectors on the required parameters. The value of the reduction in the payment for electric energy was taken as the income for the households. The economic efficiency was calculated based on the forecasted average electricity tariff, taking into account inflation from 2 to 16 %. The payback of a solar hot water heating system depends primarily on the cost of purchase, installation of equipment and on the discount rate. The practical significance is to substantiate the economic efficiency of solar collectors for consumers. The methodology and results of the study can be used in private residential construction and in justification of the use of alternative energy sources for Russian regions with low insolation.
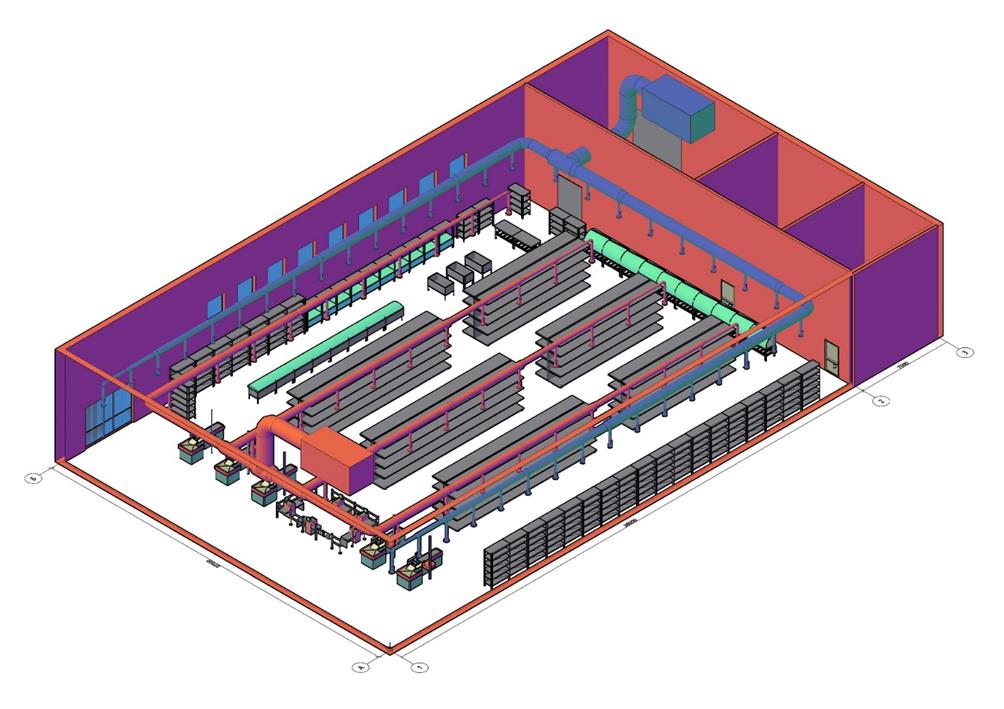
Effective management of the ventilation system is one of the main priorities for improving the energy efficiency of public buildings today. There are two types of energy saving in ventilation systems. The first is saving electrical energy, the second is saving thermal energy. For the desighned shopping centre "Magnit" (Tyumen) the authors proposed the ventilation system with intermittent operation. In the ventilation system of the desighned building, we calculated and selected energy consuming equipment of Russian manufacturers. The airflow rate of the ventilation system depends on the number of visitors and takes into account the irregularity of visits to the designed shopping centre. A graph of the distribution of the required airflow rate by period was plotted. An automation scheme for the ventilation system was proposed. The consumption of electricity of the ventilation system with intermittent operation during the year and the annual heat consumption were calculated. Calculations showed that the annual energy cost for ventilation system with intermittent operation in the projected building would be 1.72 times less than for the permanent system, the equipment would pay off in 0.4 years. Thus, it is possible to speak about the effective application of ventilation system with intermittent operation in the designed buildings with irregularity of visits.
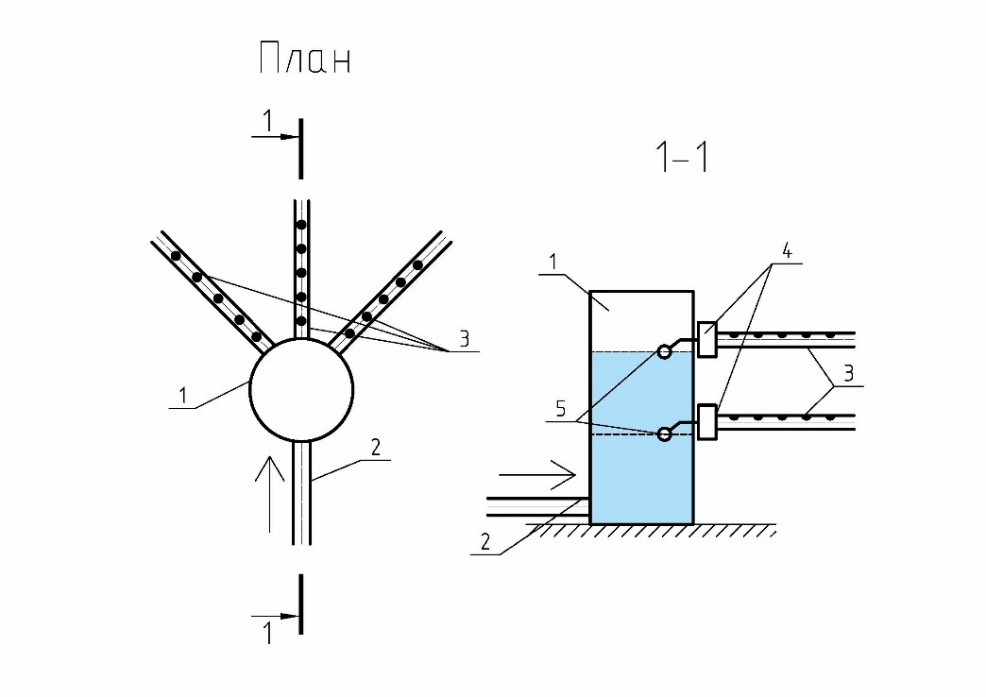
When producing water using desalination technologies, significant volumes of highly concentrated brines are formed. The solution of the problem of wastes recycling is an important global issue for water protection organizations, and the studies of the last decade confirm this. The article discusses an environmentally friendly method of dispersed uniform brine discharge into the water area, presents the developed technical solution and describes the principle of its operation. As an example, the authors calculate the hole diameters of the distribution pipeline for uniform brine discharge along the length. We calculated the radius and the scattering jet rate at a given distance from the hole in the distribution pipeline. The difference in brine salt concentrations at a depth of 20 m from the discharge point between the background concentration in the sea and the salt concentration was found to be from 0.439 % to 0.524 % along the length of the discharge pipeline. Dissolution of brines to safe concentrations becomes even more intense in the presence of sea currents. The research results can be used in the design and operation of such systems.
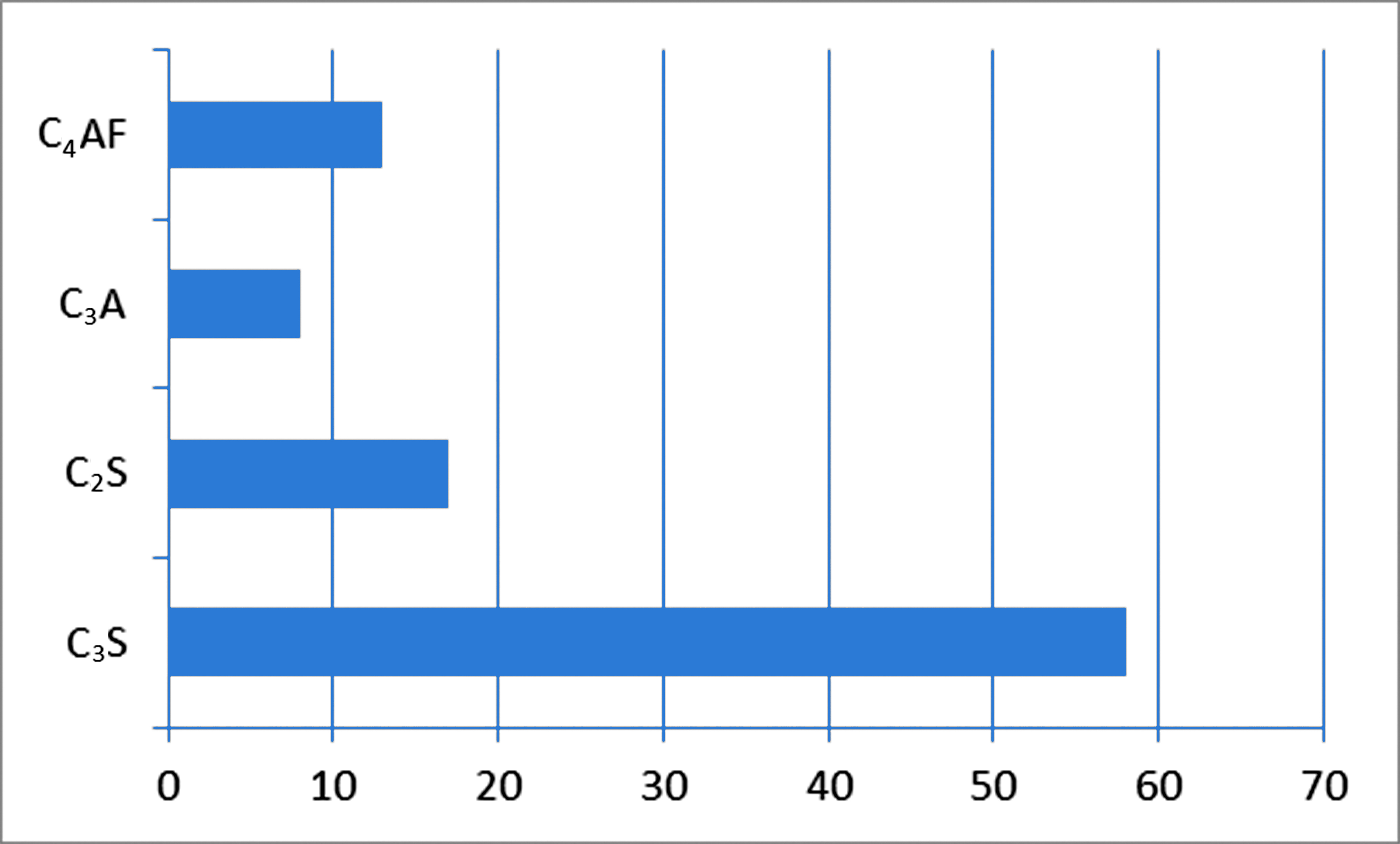
Introduction of complex antifreezes based on calcium formate, calcium chloride and superplasticizer Polyplast SP-1 into cement masses leads to changes in the phase composition of cement mortars. Of great importance are the developments of complex modifiers that are used for the hardening phase of cement-crushed mixtures, especially at low temperatures (down to –20 °C). The phase and structural characteristics of cement mortars have not been sufficiently studied. In this regard, the work investigated the effect of complex antifreeze additives on the properties and phase composition during the structuring of cement masses. Compressive strength reaches its maximum value (44.8 MPa) with the addition of calcium formate, calcium chloride and superplasticizer to the composition of cement pastes. X-ray diffraction analysis was carried out using a DRON-3 diffractometer. The used methods were standard. The X-ray diffraction patterns of the samples prove the high intensity of reflections of calcium hydrosilicate d = 9.69 Å, portlandite d = 4.921 Å, d = 2.632 Å, which indicates a high degree of hydration of portland cement. The combined use of calcium formate and calcium chloride promotes the activation of hydrolysis, and the addition of superplasticizer SP-1 leads to a decrease in the water-cement ratio to 0.20, which leads to an acceleration of the hardening process. Complex antifreeze additives increase the percentage ratio of crystalline phase to amorphous phase, thus, cement pastes with complex additives of 6 % (HCOO)2Ca, 3 % CaCl2, 2 % SP-1 have the highest value of degree of hydration (0.70) due to the formation of 63 % crystalline phase. Newly formed structures are typical for portlandite and dicalcium hydrosilicates. Complex antifreezes as an additive promote the activation of hydration in cement mortars, and the level of the degree of hydrolysis and the integral value of mass loss confirm this. Synergism of structure formation processes is observed at joint use of antifreeze additives in the composition of cement masses and, as a result, increases the strength of cement mortars used in construction at low climatic temperatures.
TRANSPORT
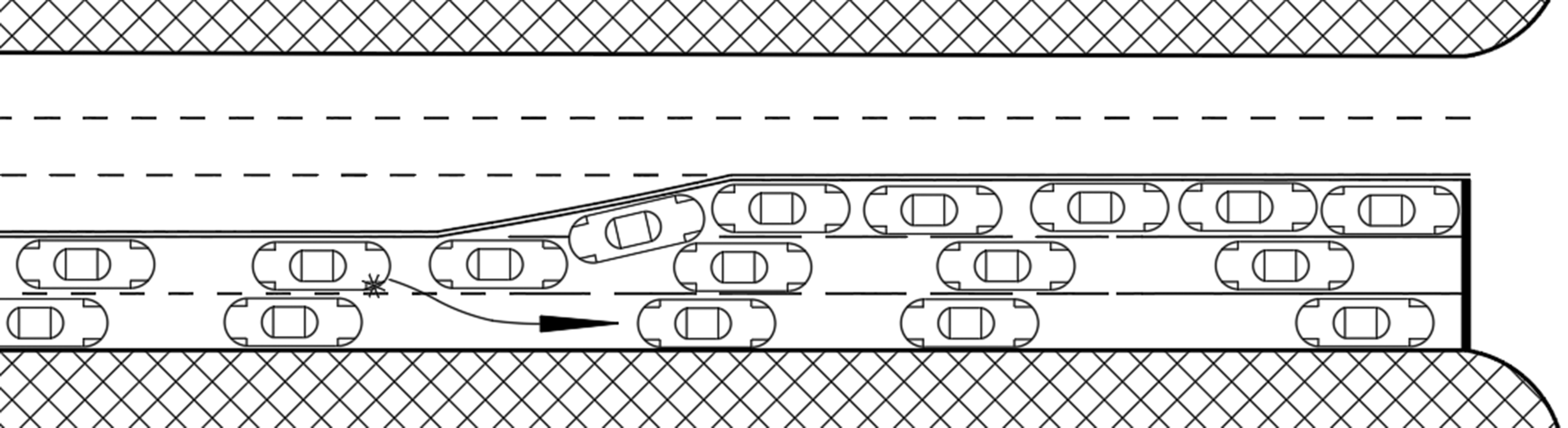
This paper continues to investigate methods for separating turning vehicle flows at urban light-controlled intersections. The authors carried out mathematical modelling of the process of left-turn transport queue formation on the basis of existing dependencies, as well as the indicator of "residual motor transport queue". After studying the processes and existing mathematical models describing the formation of a vehicle queue at a light-controlled intersection, as well as modelling of the process depending on the "residual vehicle queue" parameter, we made an assumption about the type of mathematical model describing the process. To confirm the assumptions, we carried out studies of urban light-controlled intersections in Russian cities. Based on passive experiment, it was found that the value of the residual vehicle queue obeyed the exponential distribution law of a random variable. The length of the vehicle queue formed at the intersection depends on the residual vehicle queue parameter. A linear mathematical model describes the dependence. It was found that for an average urban regulated intersection, the required rotary-accumulative lane capacity was 9 and 5 automobiles with loading factor more than and less than 1, respectively. When the residual vehicle queue increases from 5 to 50 vehicles, the size of the vehicle queue at the regulated intersection in the left-turn direction increases in 5 times. The results of the study can be used to adjust the modes of operation of urban light-controlled intersections, as well as to estimate the length of turn-accumulative lanes.
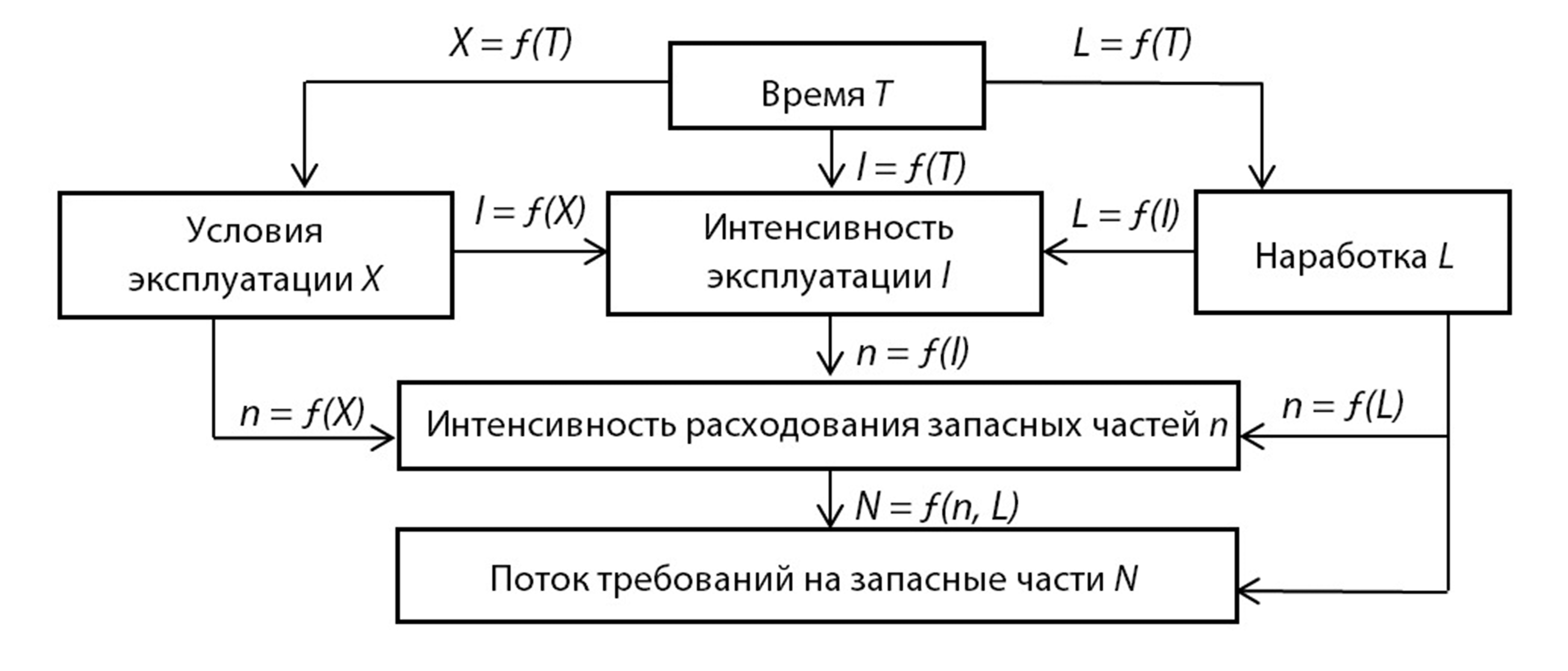
The operation of road transport is associated with maintaining the serviceability of vehicles. Companies that operate vehicles have different approaches to ensuring their serviceability. Small ones, as a rule, carry out maintenance and repair of vehicles at service stations, while large and medium-sized companies provide conditions for carrying out technical service at their own base. In this case, they are faced with the need to stock with spare parts. It was found that the costs of spare parts account for up to 45 % of all operating costs, their reduction is possible with the correct approach to planning and organization of spare parts supply. This confirms the relevance of the research. As the main factor affecting the cost of spare parts purchasing, the authors proposed to consider the reliability of car units and assemblies. A regularity was established: the reliability of a vehicle decreases with the increase of its service life, while the need for spare parts and, consequently, the purchasing cost of spare parts increases. Spare parts stocks are planned in two groups – for maintenance and repairs. It is possible to plan the consumption of spare parts for maintenance based on the vehicle fleet and on the recommendations of the manufacturer, which regulates the frequency of replacement and the list of spare parts. It is advisable to plan the nomenclature of spare parts for current repairs based on vehicles reliability. Forecasting of spare parts stock based on reliability will allow to manage spare parts stock effectively, to minimize their shelf life and to avoid the purchase of unclaimed spare parts.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
The destruction of gears occurs due to various reasons, first, connected with violation of manufacturing technology at different stages, poor quality assembly of the gear or the whole mechanism, as well as exceeding the specified operating loads. The aim of the study was to establish the causes of failure of the top drive gears in the drilling rig based on the mechanical and structural characteristics obtained by generally accepted methods, collectively used to assess the nature of the resulting damage. In order to analyze the compliance of the gear manufacturing quality with the operational requirements and to identify the cause of their failure, we carried out complex studies, including microstructural analysis of the gear metal, determination of its chemical composition and mechanical properties, as well as the study of the fracture surface morphology using scanning electron microscopy. As a result, we found that the gears failed due to a violation of the manufacturing technology in terms of wrong heat treatment.
VECTOR OF SCIENCE
About 400 normative documents were developed in the field of transportation construction, but the correctness and relevance of some of them is questionable. The lack of a unified terminology, the presence of contradictions and the increasing volume of documentation significantly complicate its use. In addition to general disadvantages, there are a number of private problems. For example, the authors point out the incorrect use of the limit states methodology for the calculation of structures, since this methodology considers limit (extreme) loads, and the regularities of the real behavior of the structure at lower levels of loads are unknown. In addition, the calculation according to limit states methodology does not take into account durability (it is not defined). When calculating using this methodology for the action of only loads with other unknown operating influences, the limit state is realized by reaching a certain limit value by this load. In reality, the limit state may occur due to changes in the shape of the structure, dimensions of cross-sections of structural elements and, more often, due to degradation of its material properties under the influence of service conditions. For the calculation of structures, it is necessary to apply the deformation approach more widely. According to it, both strength and deformation problems of structural calculation are correctly interrelated, and their hypotheses do not conflict with each other.
ISSN 2713-0770 (Online)