The scientific journal "Architecture, Construction, Transport" of open access is devoted to the consideration of a wide range of theoretical and practical issues aimed at solving problems in the field of architecture, construction and transport, and is designed to unite the efforts of researchers, experts and practitioners in searching answers to major aspects.
Our target audience is a diverse international group of readers: academics, staff and students of higher education institutions (professors, lecturers, postgraduates, students), as well as specialists and experts in construction, architecture, and transport from scientific, educational, and other organizations.
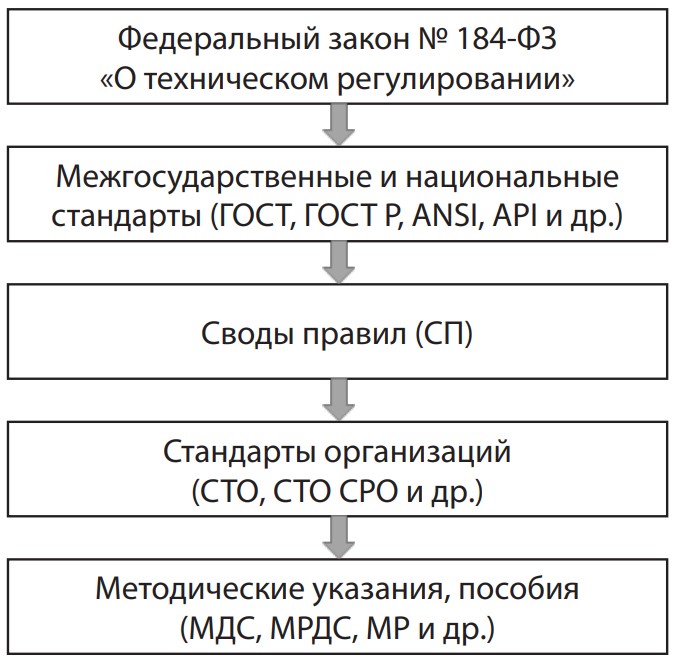
The journal "Architecture, Construction, Transport" is included in the List of peer-reviewed scientific publications in which the basic results of the candidate's or doctoral theses in the following specialties should be published:
2.1.1. Building structures, buildings, and facilities (engineering sciences)
2.1.2. Bases and foundations, underground structures (engineering sciences)
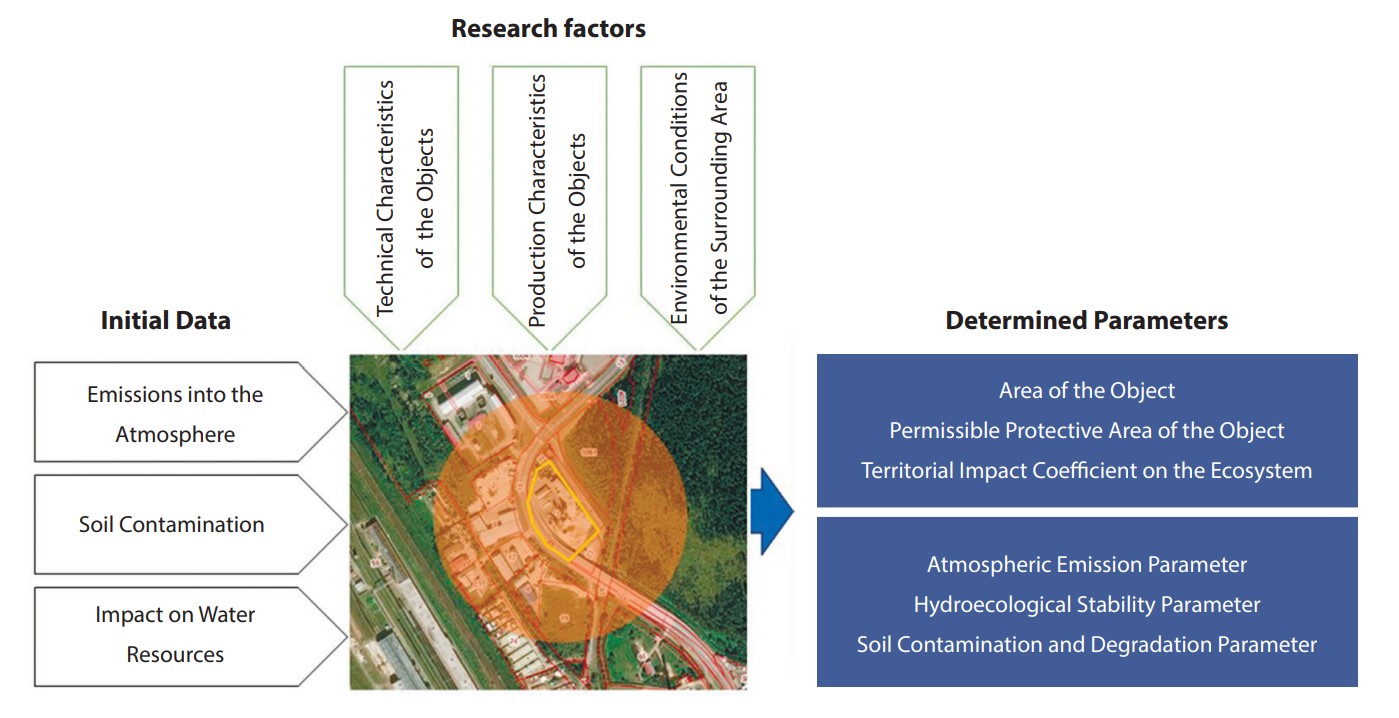
2.1.3. Heat supply, ventilation, air conditioning, gas supply, and illumination (engineering sciences)
2.1.4. Water supply and sanitation, construction systems for water resources protection (engineering sciences)
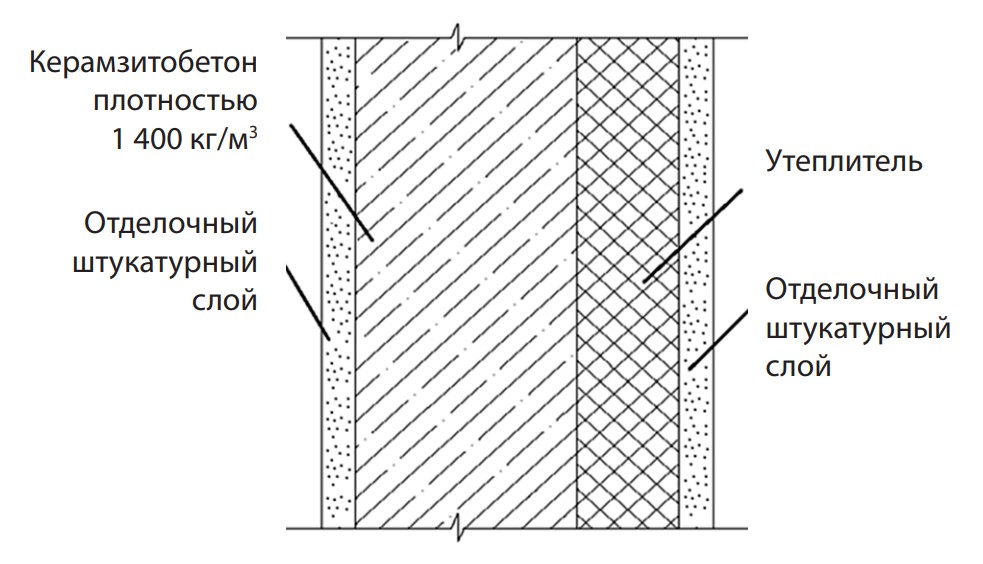
2.1.5. Construction materials and products (engineering sciences)
2.1.8. Design and construction of roads, subways, airfields, bridges, and transportation tunnels (engineering sciences)
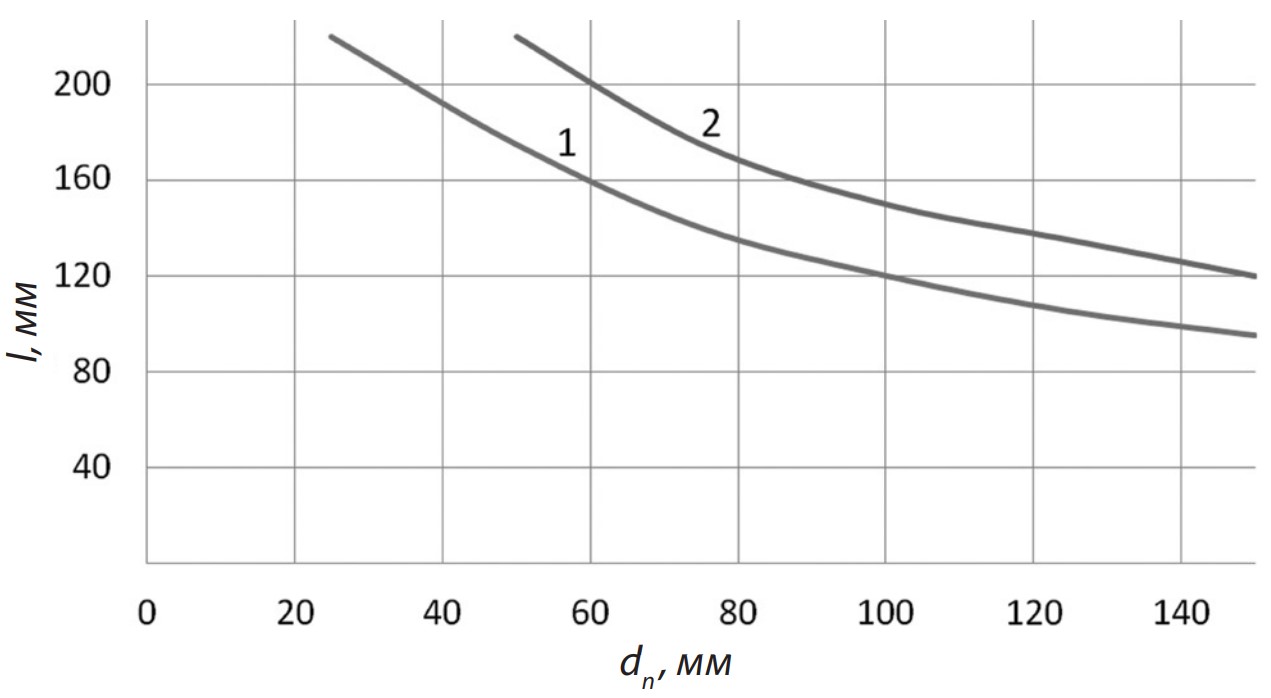
2.1.9. Structural mechanics (engineering sciences)
2.1.11. Theory and history of architecture, restoration and reconstruction of historical and architectural heritage (architecture, engineering sciences)
2.1.12. Architecture of buildings and structures. Creative concepts of architectural activity (architecture, engineering sciences)
2.9.5. Road transport operation (engineering sciences)
Also, the editors accept for publication materials on specialties:
2.5.5. Technology and equipment for mechanical, physical and technical processing (engineering sciences)
2.5.6. Mechanical engineering technology (engineering sciences)
Indexation of publication: included in the Russian project RISC, indexed in the international database DOAJ, ROAD, in the All-Russian Institute for Scientific and Technical Information of the RAS database, presented on the Lens.org and Semantic Scholar platforms, in the open database of scientific literature OpenAlex, full texts of articles are posted in the "CyberLeninka" scientific electronic library, on the RCSI Journals Platform.
The journal participates in the international CrossRef project, including using the CrossMark service to maintain the content it publishes and to alerting readers to changes if and when they occur.
Languages of publications: Russian, English.
Scientific articles are published in the journal for free.
Access to all articles is open. The journal adheres to the Budapest Open Access Initiative.
Articles are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The Journal is registered in the Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technology and Mass Media. Registration number: PI No. FS77-80657 dated from 07.04.2021.
Current issue
ARCHITECTURE
CONSTRUCTION
TRANSPORT
Announcements
2025-11-28
Тюменский рынок недвижимости замедляется?
13 ноября прошло очередное заседание пресс-клуба Союза строителей. Представители Главного управления строительства Тюменской области, Администрации города Тюмени, застройщиков, риэлторов, специалисты-аналитики рынка недвижимости и ипотечного кредитования обсудили текущую ситуацию, поделились сомнениями и планами на будущее.
| More Announcements... |